Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange or currency trading, is the act of buying and selling currencies on the global market. It’s one of the largest financial markets in the world, with an immense daily trading volume that surpasses even the stock market. Understanding the forex market, how it operates, its participants, and the mechanics of trading currencies in pairs are crucial for anyone looking to dive into this fast-paced trading environment.
Understanding the Forex Market
The forex market is where currencies are traded 24 hours a day, five days a week, across almost every time zone. Unlike stocks, which are traded on centralized exchanges, forex trading occurs directly between two parties in an over-the-counter (OTC) market. The market is run by a global network of banks and financial institutions, making it accessible from anywhere in the world.
How It Works
Forex trading involves exchanging one currency for another, with the aim of making a profit from changes in exchange rates. These changes are influenced by various factors, including economic indicators, market sentiment, political events, and interest rates.
Participants in the Forex Market
The forex market has a wide range of participants, from central banks and financial institutions to individual retail traders. Each participant plays a role in determining the exchange rates based on supply and demand dynamics.
- Central Banks: Can influence their national currency’s value through monetary policy.
- Banks and Financial Institutions: Participate in the market for currency conversion and speculative trading.
- Corporations: Engage in forex trading as part of their international business operations.
- Retail Traders: Individuals trade on the forex market primarily for speculative reasons, using brokers to access the market.
Trading Currencies in Pairs
Currencies are traded in pairs, such as EUR/USD or USD/JPY. Each pair consists of a base currency and a quote currency, with the exchange rate reflecting how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency.
- Base Currency: The first currency listed in the pair.
- Quote Currency: The second currency in the pair.
For example, if the EUR/USD exchange rate is 1.1800, it means 1 Euro can be exchanged for 1.1800 US dollars.
Understanding Exchange Rates
Exchange rates fluctuate based on economic factors, geopolitical stability, and market sentiment. Traders make profits by predicting these fluctuations, buying currencies they believe will strengthen and selling those they expect to weaken.
- Direct Quote: Represents the domestic currency per unit of the foreign currency.
- Indirect Quote: Represents the foreign currency per unit of the domestic currency.

Choosing a Forex Broker
In the realm of forex trading, selecting the right broker is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your trading experience and success. A forex broker acts as an intermediary between the retail trader and the forex market, providing access to trading platforms where currencies can be bought and sold. Given the multitude of brokers available, it’s essential to consider several key factors to ensure that you choose a broker that aligns with your trading needs and goals.
Regulation
One of the most critical factors in choosing a forex broker is regulation. A regulated broker adheres to strict standards set by regulatory authorities, providing traders with a level of protection and security.
- Why It Matters: Regulation ensures that the broker operates with transparency and fairness, safeguarding your funds from fraudulent practices.
- What to Look For: Check that the broker is regulated by reputable regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), the National Futures Association (NFA) in the United States, the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK, or other relevant authorities in the broker’s operating countries.
Spreads
The spread, which is the difference between the bid (sell) and ask (buy) price of a currency pair, directly affects the cost of trading. Lower spreads can significantly reduce trading costs, especially for active traders.
- Why It Matters: A lower spread means you pay less to the broker for each trade, which can lead to higher profitability.
- What to Look For: Compare the spreads for different currency pairs across brokers, especially for the pairs you are most interested in trading.
Leverage
Leverage allows traders to control a larger position with a smaller amount of money. While it can amplify profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses.
- Why It Matters: Understanding and managing leverage is crucial in forex trading, as misuse can lead to rapid losses.
- What to Look For: Look for a broker that offers flexible leverage options that match your risk tolerance and trading strategy. It’s also important to understand the broker’s margin requirements and margin call policies.
Trading Platform
The trading platform is your primary tool for conducting trades, analyzing the market, and managing your account. Usability, features, and reliability are key considerations.
- Why It Matters: A robust, user-friendly platform enhances your trading experience and effectiveness.
- What to Look For: Evaluate the platform’s ease of use, available technical and fundamental analysis tools, execution speed, and stability. Many brokers offer demo accounts, allowing you to test the platform before committing.
Additional Considerations
- Customer Support: Responsive and knowledgeable customer support is crucial, especially for new traders who may need assistance.
- Account Types and Requirements: Consider the minimum deposit requirements, account types offered, and whether the broker provides accounts that suit your trading style and goals.
- Educational Resources: Access to high-quality educational materials and market analysis can be invaluable, particularly for those new to forex trading.
Analyzing the Forex Market
Successful forex trading hinges on the ability to analyze and interpret market movements accurately. Traders use two main types of analysis to forecast future currency movements and make informed trading decisions: fundamental analysis and technical analysis. Each approach offers unique insights into the forex market, leveraging different data sets and methodologies to predict currency price movements. Understanding these analyses is crucial for anyone engaged in forex trading, providing the tools needed to navigate the complexities of the global currency market.
Fundamental Analysis in Forex Trading
Fundamental analysis in forex trading involves evaluating economic indicators, interest rates, and geopolitical events to predict the movements of currency pairs. This approach is based on the premise that a country’s economic conditions directly influence its currency’s value.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators are statistics that provide insight into a country’s economic health. Key indicators include Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth rates, employment figures, retail sales, and inflation rates. Positive indicators typically bolster a currency’s value, while negative data can lead to depreciation.
Interest Rates
Interest rates set by central banks are among the most influential factors in currency valuation. Higher interest rates offer lenders higher returns relative to other countries, attracting foreign capital and causing the currency to appreciate. Conversely, lower interest rates can lead to currency depreciation.
Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events such as elections, trade negotiations, and conflicts can significantly impact currency markets. Traders closely monitor such events, as they can lead to increased volatility and create trading opportunities.

Technical Analysis in Forex Trading
Technical analysis involves studying historical currency price movements and trading volumes to identify trends and predict future movements. This analysis relies on charts, indicators, and patterns to make trading decisions.
Charts
Charts are the cornerstone of technical analysis, providing a visual representation of currency price movements over time. Traders use different chart types, including line, bar, and candlestick charts, to identify trends and market sentiment.
Indicators
Technical indicators are mathematical calculations based on price, volume, or open interest, used to forecast market direction. Common indicators include moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), and Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD). These tools help traders identify trends, momentum, and potential reversal points.
Patterns
Chart patterns such as head and shoulders, triangles, and flags signify potential market movements based on past price formations. Traders use these patterns to identify entry and exit points, as well as to set stop-loss orders.
Understanding and Using Leverage Wisely in Forex Trading
Leverage is a powerful tool in forex trading, allowing traders to control large positions with a relatively small amount of capital. It amplifies both potential profits and losses, making it a double-edged sword that must be used with caution and understanding. This article explores how leverage works in forex trading, its impact on trading capital, the risks associated with high leverage, and strategies for managing those risks effectively.
How Leverage Works in Forex Trading
In forex trading, leverage is expressed as a ratio, such as 50:1, 100:1, or even higher. This ratio represents the amount of money you can control with a specific amount of trading capital. For example, with 100:1 leverage, you can control a position worth $100,000 with just $1,000 of your own capital.
Leverage is essentially a loan provided by the broker to the trader, enabling the trader to open larger positions than their capital would ordinarily allow. It’s designed to increase the potential return on investment, but it also increases the potential for significant losses.
Impact on Trading Capital
Leverage can dramatically amplify the gains from successful trades. Even small movements in currency prices can result in significant profits when trading with high leverage. However, the converse is also true—losses can quickly deplete trading capital when a leveraged position moves against the trader.
Example:
- Without leverage: A 1% movement on a $1,000 position results in a $10 profit or loss.
- With 100:1 leverage: The same 1% movement on a $100,000 position (controlled with $1,000 of capital) results in a $1,000 profit or loss, equating to a 100% gain or loss on the initial capital.
Risks Associated with High Leverage
While leverage can increase the potential for substantial profits, it also raises the risk level. High leverage can lead to rapid losses, especially in the volatile forex market, where currency prices can fluctuate widely in short periods.
- Margin Calls: If the market moves against a highly leveraged position, traders may face margin calls, requiring them to deposit additional funds to keep the position open.
- Liquidation: If a trader cannot meet a margin call, the broker may close the position, resulting in a total loss of the initial capital.
Managing Leverage Risks
Wise use of leverage is critical for sustainable forex trading. Here are strategies to manage the risks associated with leverage:
- Understand Leverage: Before trading with leverage, ensure you fully understand how it works and its potential impact on your trades.
- Use Lower Leverage: Opting for lower leverage ratios can help manage risk, especially for beginners or in highly volatile market conditions.
- Implement Risk Management Strategies: Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on leveraged positions. Determine your risk tolerance and set stop-loss orders accordingly to protect your capital.
- Practice Money Management: Never invest more than you can afford to lose. Effective money management involves only using a small percentage of your total capital for each leveraged trade.
Developing a Forex Trading Strategy
A successful forex trading journey hinges on the development and execution of a well-thought-out trading strategy. In the dynamic world of forex trading, where currency values fluctuate due to various global events and economic indicators, having a clear strategy not only guides trading decisions but also helps manage risk and emotions. This article explores different types of trading strategies, emphasizing the importance of a solid trading plan and the discipline to adhere to it.
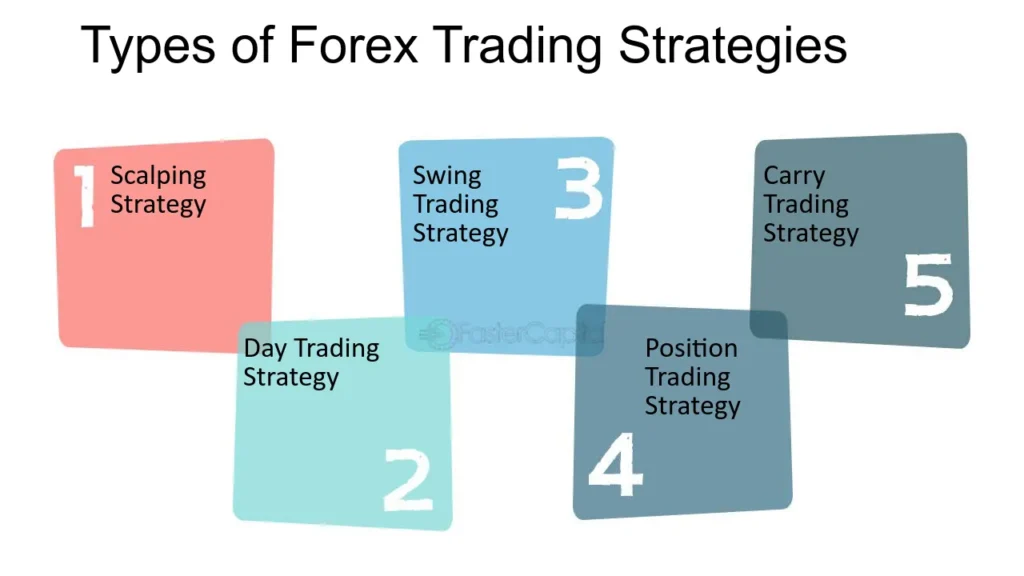
Types of Trading Strategies for Forex Trading
Forex traders often adopt specific trading styles or strategies based on their goals, risk tolerance, and the time they can dedicate to the markets. Here are three primary trading strategies commonly used:
Day Trading
Day trading is the practice of buying and selling positions within the same trading day, targeting short-term market movements for profit. These traders usually employ technical analysis to inform their swift decision-making. To augment their trading capital, they often leverage financial instruments, maximizing potential gains from small market changes.
- Characteristics: Requires constant market monitoring and quick decision-making. It suits traders who can dedicate the entire trading day to this activity.
- Risk Management: Due to the fast-paced nature and use of leverage, effective risk management and a strict exit strategy are crucial.
Swing Trading
Swing trading is a medium-term strategy, where positions are held for several days to weeks, aiming to capitalize on market trends’ “swings”. This approach blends technical analysis with fundamental insights to pinpoint potential trend reversals or continuation patterns. By diversifying the sentence structures, the text becomes more engaging and dynamic.
- Characteristics: Less time-intensive than day trading, suitable for those who cannot trade full-time.
- Risk Management: Involves setting wider stop-loss orders to account for overnight and weekend market gaps.
Position Trading
Position trading stands as a long-term strategy, primarily centered on fundamental factors, with trades enduring from several weeks to months, sometimes extending to years. Its practitioners aim to capitalize on significant currency trends, steering clear of the noise from short-term fluctuations. This approach allows traders to focus on the bigger picture, seeking substantial gains over extended periods.
- Characteristics: Requires a deep understanding of macroeconomic fundamentals driving currency values. It’s suited for patient traders comfortable with holding positions for extended periods.
- Risk Management: Involves a thorough analysis of geopolitical and economic indicators. Stop losses are typically wider to withstand market volatility.
The Importance of a Solid Trading Plan
A trading plan outlines your financial goals, risk tolerance, trading strategies, and criteria for entering and exiting trades. It serves as a blueprint for making disciplined and rational trading decisions, helping to avoid emotional trading and impulsive reactions to market noise.
Components of a Trading Plan
- Trading Goals: Define what you aim to achieve through forex trading, setting realistic and measurable objectives.
- Risk Management: Determine your risk tolerance and how you will manage risk on each trade, including setting stop-loss levels and deciding how much capital to risk on a single trade.
- Analysis Methods: Outline the technical indicators, chart patterns, or economic indicators you will use to make trading decisions.
- Entry and Exit Criteria: Specify the conditions that must be met before entering or exiting a trade.
Sticking to Your Trading Plan
Discipline is key to successful forex trading. Once you have developed a trading plan:
- Consistency: Follow your plan consistently, resisting the temptation to chase losses or deviate from your strategy based on emotions or market rumors.
- Review and Adjust: Regularly review your trading performance and strategy effectiveness. Be open to making adjustments as you gain more experience and as market conditions evolve.

Risk Management in Forex Trading
Risk management is an essential aspect of successful forex trading. Given the market’s high volatility and the use of leverage, the potential for both significant gains and losses is magnified. Effective risk management strategies help traders minimize losses, protect trading capital, and navigate the psychological challenges of trading. This article explores key techniques for managing risk in forex trading, emphasizing the importance of discipline in maintaining a healthy trading mindset.
Techniques for Managing Risk
Stop-Loss Orders
A stop-loss order is an instruction to close out a trade at a specific price to prevent further losses if the market moves against your position. It’s one of the most fundamental risk management tools available to forex traders.
- Fixed Stop-Loss: Set at a predetermined level away from the opening price.
- Trailing Stop-Loss: Adjusts automatically with market movements, locking in profits while protecting against reversals.
Position Sizing
Position sizing involves determining how much capital to allocate to a trade based on your risk tolerance and the stop-loss level. It ensures that losses on individual trades do not significantly impact the overall trading account.
- Percentage Risk Method: Allocates a specific percentage of the total trading account to each trade.
- Volatility-Based Sizing: Adjusts position size based on the currency pair’s current volatility, allowing for wider stop-losses on more volatile pairs.
Diversification
While diversification is more challenging in forex trading, given its focus on currency pairs, it can still be achieved by:
- Trading Multiple Pairs: Spread risk across currency pairs from different countries or regions.
- Varying Trading Strategies: Employ different trading strategies (e.g., day trading, swing trading) to capitalize on various market conditions.

The Psychological Aspects of Trading
The psychological challenges of forex trading, such as fear, greed, and stress, can significantly impact decision-making. Maintaining discipline is crucial for managing these emotional aspects and adhering to your trading strategy.
Techniques for Maintaining Discipline
- Develop a Trading Plan: Outline your strategy, risk management rules, and criteria for entering and exiting trades. Stick to this plan to avoid impulsive decisions.
- Set Realistic Expectations: Understand that losses are part of trading. Setting realistic expectations helps maintain a balanced approach and prevent overtrading.
- Continuous Learning: The forex market is dynamic. Staying informed and continuously learning can boost confidence and help you make more informed decisions.
- Practice Mindfulness and Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, exercise, and ensuring a healthy work-life balance can help manage the psychological stress of trading.
Using Trading Platforms and Tools in Forex Trading
Success in forex trading is not only about understanding the market and developing strategies but also about effectively utilizing the tools and features provided by trading platforms. Platforms like MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 are among the most widely used in forex trading, offering a suite of tools that can enhance analysis, execution, and management of trades. Familiarizing yourself with these platforms and their functionalities is crucial for maximizing your trading potential.

Familiarizing Yourself with Trading Platforms
MetaTrader 4 (MT4)
MT4 is highly regarded for its user-friendly interface, robust functionality, and flexibility. It caters to traders of all levels, providing:
- Advanced Charting Tools: MT4 offers comprehensive charting capabilities, enabling traders to analyze market trends and identify trading opportunities.
- Expert Advisors (EAs): These are automated trading algorithms that can trade on your behalf based on predefined criteria.
- Custom Indicators: Apart from the standard set of technical indicators, MT4 allows the use of custom indicators tailored to specific trading strategies.
MetaTrader 5 (MT5)
While MT4 focuses primarily on forex trading, MT5 offers additional features suited for trading stocks, futures, and options, making it a more versatile platform.
- Enhanced Charting and Analysis Tools: MT5 includes more technical indicators, charting tools, and timeframes, providing a more detailed analysis of financial markets.
- Economic Calendar: Integrated directly into the platform, the economic calendar helps traders stay informed about major economic events that could impact the markets.
- Improved Order Management: MT5 allows for more types of orders than MT4, including additional pending order types and a built-in depth of market feature.
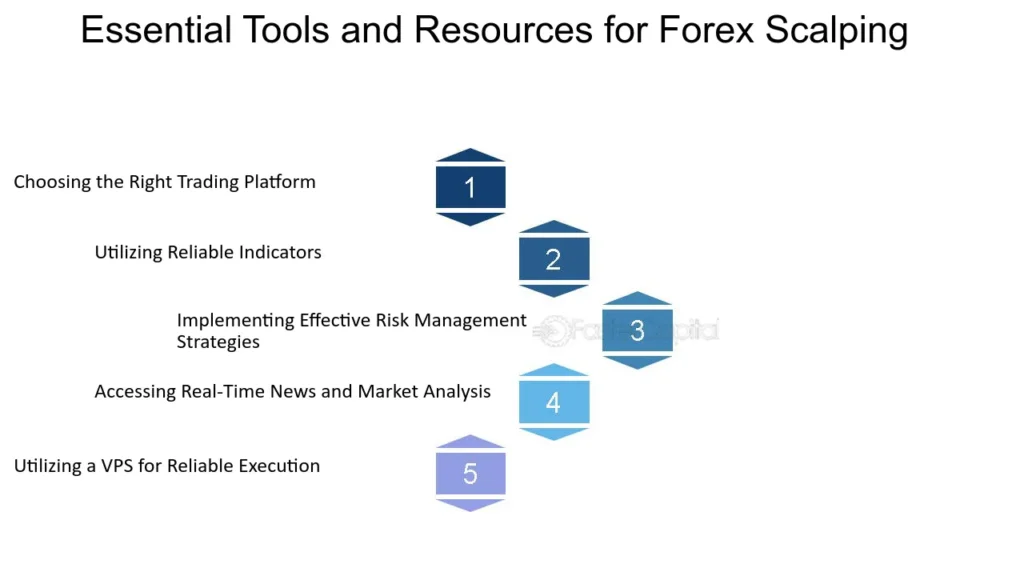
Essential Trading Tools and How to Use Them Effectively
Technical Indicators
Technical indicators are crucial for analyzing market trends and predicting future movements. Understanding how to interpret indicators like Moving Averages, RSI (Relative Strength Index), and MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) can provide insights into market sentiment and potential entry or exit points.
Economic Calendars
Staying ahead of market-moving events is essential. Economic calendars list upcoming economic reports, announcements, and other events that can affect currency values. Use this tool to plan your trading around these events, reducing the risk of being caught off-guard by market volatility.
Automated Trading Systems
For traders looking to automate their strategies, platforms like MT4 and MT5 support the development and implementation of EAs. These systems can execute trades based on predefined criteria, removing emotional bias and ensuring discipline. However, it’s important to test EAs thoroughly before deploying them in live trading environments.
Risk Management Tools
Stop-loss orders and position sizing calculators are indispensable for managing risk. Setting stop-loss orders protects your capital by automatically closing a trade at a predetermined loss threshold, while position sizing calculators help determine the optimal trade size based on your risk tolerance and account balance.

Practicing with a Demo Account in Forex Trading
Diving into forex trading can be both exciting and daunting for newcomers. Before committing real capital, it’s wise to start with a demo account—a tool offered by most forex brokers that simulates live trading with virtual money. This approach allows traders to familiarize themselves with trading platforms, test strategies, and gain confidence without the risk of losing money. Here’s why starting with a demo account is beneficial and how it can be used to refine trading strategies and skills.
Benefits of Using a Demo Account
Risk-Free Environment
Demo accounts provide a safe space to learn the mechanics of forex trading, from executing trades to understanding order types, without the financial repercussions of making mistakes in a live market.
Platform Familiarization
For traders, especially beginners, getting comfortable with trading platforms like MetaTrader 4 or 5 is crucial. Demo accounts allow users to explore and understand the features and functionalities of these platforms, ensuring they are well-prepared before entering the live markets.
Strategy Testing
One of the most significant advantages of demo trading is the ability to test and refine trading strategies. Traders can experiment with different approaches, technical indicators, and analysis methods to see what works best without any financial risk.
Psychological Preparation
Trading involves not just skill and knowledge but also psychological resilience. Practicing with a demo account helps traders experience what it feels like to see fluctuations in their account balance, albeit virtual, preparing them emotionally for the live markets.

How to Use Demo Trading Effectively
While demo accounts offer numerous benefits, maximizing their potential requires a strategic approach. Here are tips on using demo trading to improve your trading skills:
Treat It Like a Real Account
Approach trading on your demo account as if you were trading with real money. This mindset will help you take the practice seriously, making the experience more beneficial and the transition to live trading smoother.
Set Realistic Goals
Define clear objectives for what you want to achieve with demo trading, whether it’s testing a specific strategy, getting comfortable with the platform, or improving your market analysis skills.
Keep a Trading Journal
Document your trades, strategies, and observations while using the demo account. A trading journal is a valuable tool for analyzing your decisions, patterns in your trading behavior, and areas for improvement.
Gradually Transition to Live Trading
After achieving consistency in your demo trading and feeling confident in your strategy and skills, consider transitioning to live trading with a small amount of capital. Starting small allows you to experience the psychological aspects of trading with real money while minimizing potential losses.

Entering Your First Forex Trading
Making your first forex trade is a significant milestone on your trading journey. This initial step can be both exhilarating and nerve-wracking, but with the right preparation and understanding, it can also set a strong foundation for future trading endeavors. Here’s a guide to navigating your first forex trade, including key steps to follow and common mistakes to avoid, ensuring a smooth entry into the world of forex trading.
Steps for Making Your First Forex Trading
1. Educate Yourself
Before placing your first trade, ensure you have a solid understanding of forex market principles, currency pairs, how trades are executed, and the factors that influence currency movements. This knowledge is crucial for making informed trading decisions.
2. Choose a Reliable Forex Broker
Selecting the right broker is critical. Look for a broker that is regulated, offers competitive spreads, provides a user-friendly trading platform, and has a reputation for excellent customer service.
3. Set Up and Fund Your Trading Account
After choosing a broker, you’ll need to open and fund your trading account. Be mindful of the minimum deposit requirements and consider starting with an amount you’re comfortable potentially losing as you learn.
4. Familiarize Yourself with the Trading Platform
Spend time getting to know the trading platform (e.g., MetaTrader 4/5). Understand how to execute trades, set stop-loss and take-profit orders, and use any available tools and indicators.
5. Start with a Demo Account
Before trading with real money, practice with a demo account. This practice allows you to get a feel for the market and test your trading strategy without financial risk.
6. Develop a Trading Plan
A solid trading plan should outline your trading goals, risk tolerance, strategy, and criteria for entering and exiting trades. This plan will guide your trading decisions and help maintain discipline.
7. Analyze the Market
Using fundamental and technical analysis, identify potential trading opportunities. Consider economic indicators, news events, and chart patterns that might affect currency values.
8. Place Your First Trade
Once you’ve identified a trading opportunity and are comfortable with your analysis, it’s time to place your first trade. Decide on the currency pair, determine your position size, set your stop-loss and take-profit orders, and execute the trade.
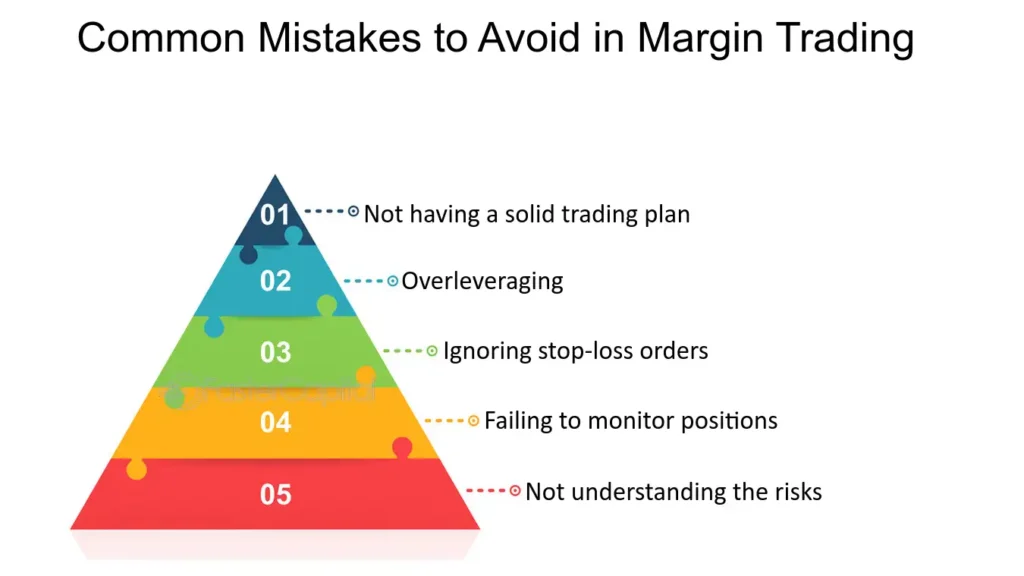
Common Mistakes to Avoid as a Beginner Trader
- Overleveraging: While leverage can amplify gains, it can also magnify losses, especially for beginners. Use leverage cautiously and understand the risks.
- Ignoring Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders help manage risk by automatically closing a trade at a predetermined loss threshold. Failing to set stop-losses can lead to significant, unchecked losses.
- Letting Emotions Drive Trading Decisions: Emotional trading often leads to impulsive decisions. Stick to your trading plan and make decisions based on analysis, not emotions.
- Overtrading: Placing too many trades or trading with too much volume can erode profits through fees and lead to decision fatigue. Quality over quantity is key in forex trading.
- Neglecting Education: The forex market is complex and constantly evolving. Continuous learning and adapting are essential for long-term success.
Continuing Education and Staying Informed in Forex Trading
The journey of a forex trader is one of continuous learning and adaptation. The volatile nature of the forex market demands not just an understanding of its fundamentals but also an ongoing commitment to education and staying informed about global economic events. This commitment enables traders to refine their strategies, make informed decisions, and remain competitive. Here’s how traders can engage in continuing education and the importance of staying updated with market news and economic events.
Resources for Further Learning
Webinars and Online Courses
Many forex brokers and financial education platforms offer webinars and online courses covering various aspects of forex trading. These resources range from beginner to advanced levels, providing insights into market analysis, trading strategies, risk management, and psychological aspects of trading.
- Benefits: Interactive webinars allow for real-time questions and answers, while structured courses offer comprehensive learning at your own pace.
- What to Look For: Seek out courses and webinars led by experienced traders or recognized financial educators, focusing on topics relevant to your trading style and goals.
Trading Communities
Joining trading communities or forums can be an excellent way to learn from more experienced traders, share strategies, and discuss market trends. Many communities offer valuable discussions on technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and trading experiences.
- Benefits: Being part of a community fosters a sense of support and can provide new perspectives on trading challenges and opportunities.
- What to Look For: Look for active, well-moderated communities with a focus on constructive, informative discussions.
Books and Publications
A wealth of knowledge can be found in trading books and financial publications. These resources offer deep dives into specific trading methodologies, economic theories, and the psychological aspects of trading.
- Benefits: Books provide detailed insights and strategies that have been successful for experienced traders and analysts.
- What to Look For: Prioritize books and publications with high ratings and reviews from the trading community, especially those that have stood the test of time.

Staying Updated with Market News and Economic Events
The forex market is significantly influenced by global economic events, political developments, and financial news. Staying informed is crucial for making timely and effective trading decisions.
Economic Calendars
Use economic calendars to track important events like central bank meetings, employment reports, and GDP releases. These events can cause significant market movements, offering trading opportunities.
Financial News Websites
Regularly follow reputable financial news websites and platforms for the latest market news, analysis, and expert opinions. Being well-informed allows you to anticipate market movements and adjust your trading strategies accordingly.
Mobile Apps and Alerts
Leverage mobile apps and alerts from financial news outlets or your forex broker to receive real-time updates on market conditions and economic events. This ensures you never miss critical information that could impact your trades.

FAQs:
- What Is Forex Trading?
- Forex trading involves exchanging one currency for another, predicting currency price movements to make a profit.
- How Do I Choose a Forex Broker?
- Look for brokers that are regulated by reputable bodies, offer competitive spreads, provide a reliable trading platform, and support leverage settings that match your risk tolerance.
- What’s the Difference Between Fundamental and Technical Analysis?
- Fundamental analysis focuses on economic and political factors affecting currency values, while technical analysis uses historical price data and charts to predict future movements.
- Why Is Leverage Considered Risky in Forex Trading?
- Leverage can amplify both profits and losses, making it possible to lose more than your initial investment if not used carefully.
- How Can I Manage Risk in Forex Trading?
- Implement risk management techniques like setting stop-loss orders, managing position sizes, and never risking more than a small percentage of your account on a single trade.
- Should I Use a Demo Account Before Trading Live?
- Yes, demo accounts offer a risk-free way to practice trading, test strategies, and familiarize yourself with the trading platform without using real money.
- What Are the Most Common Trading Strategies?
- Common strategies include day trading (making trades within a single day), swing trading (holding positions for several days to weeks), and position trading (holding positions for months to years).
- How Important Is It to Stay Updated with Forex News?
- Very important, as forex markets can be highly responsive to economic news and geopolitical events, which can affect currency values.
- Can I Start Forex Trading with a Small Amount of Money?
- Yes, many brokers offer micro or mini accounts that allow you to start trading with a small amount of capital.
- What Should I Do if I’m Consistently Losing Money?
- Reevaluate your trading strategy, ensure you’re following risk management practices, consider further education, and maybe take a break to reassess your approach.

