Embarking on the journey of stock trading can be both exhilarating and daunting for beginners. The stock market, a central hub of financial activity, plays a pivotal role in the global economy, influencing both individual fortunes and the financial health of nations. This chapter aims to demystify the basics of the stock market, its significance, and the indispensable role brokers play in navigating this dynamic arena.
Basics of the Stock Market and Its Importance for Best stock brokers
The stock market is a complex network where shares of publicly held companies are bought, sold, and traded. At its core, it facilitates the exchange of capital between investors and companies, serving as a critical mechanism for companies to raise funds for expansion and operations.
Understanding Stocks and Shares
A stock, or a share, represents a fraction of ownership in a company. When you buy a company’s stock, you’re buying a piece of that company, including the right to a portion of its profits and any voting rights attached to the stock.
Why the Stock Market Matters
The stock market is vital for several reasons:
- Economic Indicator: The overall performance of the stock market is often seen as an indicator of a country’s economic health.
- Wealth Creation: It offers individuals and institutions the opportunity to invest in companies, potentially leading to wealth creation over time.
- Liquidity: The stock market provides liquidity, enabling investors to buy and sell securities easily.
- Corporate Finance: For companies, it’s a means to raise capital without incurring debt, by selling shares to the public.
The Role of Best stock brokers Trading
Brokers act as intermediaries between investors and the stock market. They are authorized to buy and sell securities on behalf of their clients and play a crucial role, especially for beginners venturing into stock trading.
How Best stock brokers Facilitate Trading
- Access to the Market: Best stock brokers provide the platform and tools necessary for traders to access stock exchanges.
- Advice and Research: Many brokers offer research services, market analysis, and investment advice, helping beginners make informed decisions.
- Execution of Trades: They execute buy and sell orders, ensuring the best possible price for their clients.
- Account Management: Brokers offer various account types and can help manage investments based on the client’s financial goals.
Choosing the Best stock brokers
Selecting the right broker is a foundational step in your stock trading journey. Consider factors such as commission fees, available tools and resources, the user-friendliness of the trading platform, and the level of customer support provided.

Criteria for Choosing a Beginner-Friendly Best stock brokers
For newcomers to the stock market, selecting a broker is a critical decision that can influence your trading experience and success. A beginner-friendly broker not only provides a gateway to the market but also supports your learning curve and growth as a trader. Here are the essential features and services to look for when choosing a broker that benefits beginners.
User-Friendly Trading Platform
The trading platform is your primary tool for conducting trades, analyzing the market, and managing your portfolio. A beginner-friendly platform should be:
- Intuitive: Easy navigation and a clean interface help prevent overwhelming beginners.
- Reliable: Platform stability is crucial for timely execution of trades, especially in volatile markets.
- Educational Resources: Access to tutorials, guides, and FAQs directly within the platform can be highly beneficial.
Comprehensive Educational Materials
A commitment to educating clients is a hallmark of a beginner-friendly broker. Look for:
- Trading Basics: Guides and articles that cover fundamental trading concepts and terminology.
- Webinars and Workshops: Live sessions provide insights into market analysis and trading strategies.
- Demo Account: A risk-free account where you can practice trading with virtual money is invaluable for gaining experience without financial risk.
Strong Customer Support
Beginners will likely have questions and encounter issues as they start trading. Effective customer support can significantly enhance the learning experience:
- Availability: 24/5 support is standard in the trading world, but 24/7 support is a plus.
- Multiple Channels: Look for brokers offering support via phone, email, live chat, and even social media.
- Quality of Service: Responsive, knowledgeable, and friendly support staff can make a big difference in your trading journey.
Low Fees and Commissions
Understanding and managing trading costs is crucial for beginners. Consider brokers that offer:
- Low Entry Point: Minimal initial deposit requirements and the option to trade in small sizes.
- Transparent Fee Structure: Clearly outlined fees for trades, account maintenance, and any other services.
- Competitive Spreads: The difference between the buying and selling price can impact your trading costs, especially if you trade frequently.
Account Types and Flexibility
A broker that offers a range of account types allows beginners to choose one that best fits their initial trading goals and capital:
- Micro or Mini Accounts: These accounts allow trading with smaller lot sizes, reducing the capital at risk.
- Scalability: As you grow more confident and your trading strategy evolves, your broker should offer account upgrades to suit your needs.
Security and Regulation
Trust and security are paramount. Ensure the broker is:
- Regulated: Look for brokers regulated by reputable authorities like the SEC, FINRA, or equivalent bodies in your country.
- Secure: Robust security measures for data protection and secure handling of funds are non-negotiable.
Additional Features
Other features that can enhance a beginner’s trading experience include:
- Market Research and Analysis: Access to market insights, news, and analysis can inform your trading decisions.
- Social Trading Platforms: Some brokers offer platforms where beginners can copy trades of more experienced investors, offering a practical learning experience.
Regulations and Safety in Stock Trading for Best stock brokers
For beginners stepping into the world of stock trading, the importance of regulations and the safety of investments cannot be overstated. The financial market is overseen by various regulatory bodies designed to maintain its integrity and protect individual investors. Understanding these entities and the significance of choosing a regulated broker is fundamental for anyone looking to navigate the stock market safely and confidently.
Understanding Regulatory Bodies
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
The SEC is a U.S. federal agency responsible for enforcing federal securities laws and regulating the nation’s stock and options exchanges and other electronic securities markets. It aims to protect investors, maintain fair, orderly, and efficient markets, and facilitate capital formation.
Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA)
FINRA is a non-governmental organization that acts as a self-regulatory body for brokerage firms and exchange markets. Its role is to write and enforce rules governing the activities of brokerage firms and brokers, protect investors, and ensure the market’s integrity.
Globally, each country has its regulatory framework and bodies, such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK, the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) in Australia, and many others, playing similar roles in their jurisdictions.

The Significance of Choosing a Regulated Best stock brokers
Investor Protection
Regulated brokers are required to comply with a set of rules and standards designed to protect investors. These include maintaining transparency in their operations, providing accurate information about investment products, and handling investor funds responsibly.
Financial Security
Regulated brokers are often required to keep clients’ funds in segregated accounts to protect them from unauthorized use and in case of the broker’s insolvency. This ensures that investors can recover their capital if the broker faces financial difficulties.
Dispute Resolution
In case of disputes or issues with transactions, investors trading with regulated brokers have access to formal dispute resolution mechanisms. Regulatory bodies can provide arbitration and mediation services to resolve conflicts between investors and brokers.
Market Integrity
Regulatory bodies monitor the activities of brokers to prevent fraud, market manipulation, and other unethical practices. Choosing a regulated broker contributes to the overall integrity and stability of the financial market.

Types of Brokerage Accounts for Beginners
As a beginner in stock trading, choosing the right type of brokerage account is a critical decision that can influence your investment strategy and financial goals. Brokerage accounts come in various forms, each with its features, risks, and benefits. This chapter explores the primary types of brokerage accounts—cash accounts, margin accounts, and retirement accounts—offering guidance on selecting the most suitable option based on individual goals and preferences.
Cash Accounts
Overview
A cash account is the most straightforward type of brokerage account, where you pay the full amount for stocks or other securities at the time of purchase. This account type is ideal for beginners due to its simplicity and lower risk profile.
Features and Benefits
- Simplicity: Transactions are conducted with available funds, making it easier to manage for those new to investing.
- Lower Risk: Without the ability to borrow funds, the risk of significant losses is minimized, offering a safer introduction to the stock market.
Margin Accounts
Overview
Margin accounts allow investors to borrow money from the broker to purchase securities, offering the potential for higher returns but also increasing the risk.
Features and Benefits
- Leverage: Provides the ability to buy more securities than you could with a cash account, potentially increasing your returns.
- Flexibility: Enables more complex trading strategies, such as short selling.
- Higher Risk: The use of borrowed money (leverage) can amplify losses, making it essential to understand the risks fully.
Retirement Accounts
Overview
Retirement accounts, such as Individual Retirement Accounts (IRAs) in the United States, offer tax advantages for long-term investing. These accounts can be either traditional, where contributions may be tax-deductible, or Roth, where withdrawals are tax-free in retirement.
Features and Benefits
- Tax Advantages: Contributions grow tax-deferred, and withdrawals are taxed at a potentially lower rate in retirement (traditional IRA) or tax-free (Roth IRA).
- Long-Term Growth: Designed for retirement savings, these accounts encourage long-term investing with compounding returns.
- Contribution Limits and Penalties: There are annual contribution limits, and early withdrawal may result in penalties, making it important to plan for long-term investment.

Guidance on Selecting the Right Account for Best stock brokers
Choosing the right brokerage account depends on your investment goals, risk tolerance, and financial situation:
- For Beginners and Low-Risk Tolerance: A cash account is recommended due to its simplicity and lower risk. It offers a solid foundation for learning about stock trading without the complexities of borrowing funds.
- For Those Seeking Higher Returns with Acceptable Risk: A margin account may be suitable if you’re comfortable with the higher risk and have a clear understanding of how margin works, including the potential for greater losses.
- For Long-Term Investors Focused on Retirement: Retirement accounts offer significant tax advantages and are ideal for those prioritizing long-term growth and retirement savings.
Understanding Broker Fees and Commission Structures
Navigating the world of stock trading requires not only an understanding of markets and strategies but also a keen awareness of the costs associated with using brokerage services. Broker fees and commission structures can significantly impact your investment returns, especially for those just starting out. This chapter offers a detailed breakdown of potential costs and provides tips for minimizing fees and maximizing your investments.
Breakdown of Potential Costs
Trade Commissions
Trade commissions are fees charged by a broker each time you buy or sell stocks or other securities. These can vary widely between brokers, with some offering flat rates per trade and others adopting a per-share pricing model.
Account Fees
In addition to trade commissions, brokers may impose a variety of account fees, including but not limited to:
- Annual or Monthly Maintenance Fees: Charges for maintaining your brokerage account.
- Inactivity Fees: Applied if you don’t make a certain number of trades within a specified period.
- Transfer Fees: Costs associated with transferring assets in or out of your account.
- Withdrawal Fees: Charges for taking money out of your account.
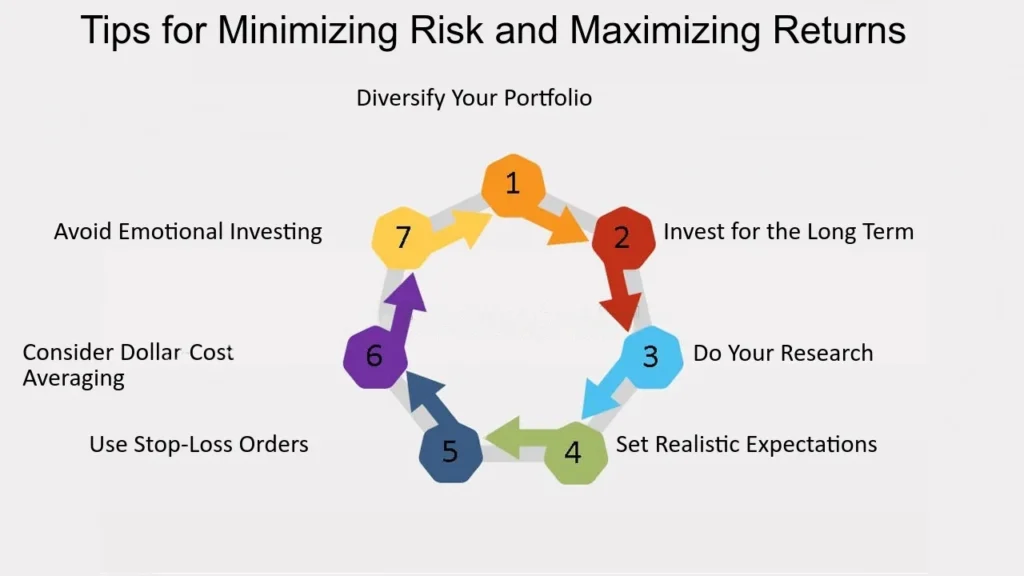
Tips for Minimizing Fees and Maximizing Investments
1. Choose a Best stock brokers with a Favorable Fee Structure
- Research and compare the fee structures of different brokers, considering both trade commissions and account fees. Online brokers often offer competitive rates and are a good starting point for beginners.
2. Consider Commission-Free Best stock brokers
- Some brokers offer commission-free trades on stocks and ETFs, which can significantly reduce your trading costs. Be sure to understand how these brokers make money (e.g., payment for order flow, interest on cash balances) to assess any potential conflicts of interest.
3. Watch Out for Account Fees
- Read the fine print and be aware of all possible account fees. Some brokers offer fee waivers or discounts based on account balance or trading activity, so it’s worth asking about these options.
4. Opt for Low-Cost Index Funds and ETFs
- If your strategy includes funds, consider low-cost index funds and ETFs. These funds often have lower expense ratios compared to actively managed funds, reducing your overall costs.
5. Plan Your Trades to Minimize Costs
- Consolidating trades can reduce the number of individual transactions and, consequently, the total commissions paid. However, always balance this against the need to act on market conditions and manage risk appropriately.
6. Use Tax-Efficient Investing Strategies
- Understanding the tax implications of your investments can help you make more informed decisions that potentially lower your tax liability and improve net returns. Consider consulting a tax advisor for personalized advice.
Trading Platforms and Tools for New Investors
For those new to investing, navigating the vast array of trading platforms can be overwhelming. A user-friendly platform can make a significant difference in a beginner investor’s journey, offering ease of use, educational resources, and the tools necessary for informed trading decisions. This chapter highlights popular user-friendly trading platforms like Robinhood and E*TRADE, detailing the key features and tools new investors should look for.

User-Friendly Trading Platforms
Robinhood
Robinhood revolutionized the trading platform industry by offering commission-free trades, making it an attractive option for new investors. Its minimalist interface is designed for simplicity, facilitating easy navigation for buying and selling stocks, options, and cryptocurrency.
Key Features:
- Commission-Free Trading: Enables users to trade stocks, ETFs, options, and cryptocurrencies without transaction fees.
- Mobile-First Design: The app is intuitive, making it accessible for investors who prefer trading on their smartphones.
- No Minimum Account Balance: Allows investors to start trading with any amount, removing financial barriers to entry.
E*TRADE
E*TRADE is known for its comprehensive trading tools and resources, catering to both novice and experienced investors. It offers a wide range of investment choices, including stocks, bonds, ETFs, and mutual funds.
Key Features:
- Extensive Educational Resources: Provides a wealth of information, tutorials, and webinars to help new investors learn the basics of trading.
- Power E*TRADE Platform: Offers advanced tools for more experienced traders, while still being accessible to beginners.
- Variety of Account Types: Supports a range of investment goals, from retirement savings to active trading accounts.
Key Features and Tools to Look For
When choosing a trading platform, new investors should consider the following essential features and tools:
Educational Resources
Platforms that offer educational materials, such as tutorials, guides, and webinars, can be invaluable for beginners. These resources help demystify the stock market and investment strategies.
Ease of Use
A user-friendly interface that is intuitive to navigate is crucial for beginners. Look for platforms that provide straightforward access to buy and sell orders, portfolio overview, and market research.
Analytical Tools
Access to real-time market data, analysis tools, and charting capabilities can help new investors make informed decisions. Even simple platforms should offer basic analytical tools.
Low Costs and Fees
Consider the cost structure of the platform, including any commission fees, account maintenance fees, and costs associated with fund transfers. Platforms offering commission-free trades can significantly lower the cost barrier for new investors.
Customer Support
Reliable customer support is essential, especially for those who are still learning the ropes. Look for platforms that offer multiple support channels, including live chat, phone, and email.
Security
Ensure the platform has robust security measures in place to protect your personal and financial information. Look for features like two-factor authentication and encryption.
Educational Resources for Stock Trading Beginners
In the dynamic and often intricate world of stock trading, the availability and quality of educational resources can significantly influence a beginner’s journey toward becoming a proficient trader. Broker-provided education and training offer a foundational understanding of market principles, trading strategies, and risk management, essential for informed decision-making. This chapter discusses the importance of these resources and provides criteria for evaluating their quality and accessibility.
The Importance of Broker-Provided Education and Training
Foundation for Informed Trading
Educational resources equip beginners with the knowledge needed to navigate the stock market confidently. Understanding basic terminology, how markets operate, and factors affecting stock prices forms the basis for making informed trading decisions.
Risk Management
Trading involves inherent risks, and educational content helps beginners understand these risks and how to manage them. Learning about diversification, stop-loss orders, and position sizing can prevent significant losses.
Strategy Development
Good educational resources cover various trading strategies and their applications in different market conditions. This knowledge allows beginners to experiment with strategies in demo accounts, honing their skills without financial risk.
Regulatory Compliance
Understanding the regulatory environment is crucial for trading within legal boundaries and protecting one’s investments. Education on compliance helps traders avoid practices that could result in penalties or losses.

Evaluating the Quality and Accessibility of Educational Content
Comprehensive Coverage
Quality educational content should cover a broad range of topics, from stock market basics to advanced trading strategies, analysis techniques, and risk management. Resources that address both fundamental and technical analysis offer a well-rounded education.
Expertise and Authority
Consider the source of the information. Content created by experienced traders, financial analysts, or accredited financial educators is more likely to be reliable and valuable. Check the credentials of the contributors to ensure their expertise.
Practical Application
Resources should not only provide theoretical knowledge but also practical tools and examples. Look for content that includes case studies, real-world scenarios, and interactive elements like quizzes or simulations to apply what you’ve learned.
Updated and Relevant
The stock market and regulatory environment are continually evolving. Ensure the educational content is regularly updated to reflect the latest market trends, technologies, and regulatory changes.
Accessibility and Format
Education should be accessible in terms of both ease of access and comprehension. Good resources are available in various formats—articles, videos, webinars, eBooks, and interactive courses—to cater to different learning preferences. They should be easy to understand, avoiding overly technical language when possible.
Community and Support
Access to a community of traders or direct support from educators can enhance the learning experience. Forums, Q&A sessions, and mentorship opportunities allow beginners to clarify doubts, gain insights, and learn from the experiences of others.
Getting Started with Practice Trading Accounts
For beginners in the stock market, understanding the intricacies of trading can be daunting. This is where paper trading and demo accounts become invaluable. These practice accounts offer a risk-free environment to experiment with trading strategies, understand market movements, and gain confidence before committing real capital. This chapter explores the benefits of using such accounts and provides guidance on utilizing them effectively.
The Benefits of Paper Trading or Using Demo Accounts
Risk-Free Learning Environment
The most significant advantage of demo accounts is the ability to learn without the risk of losing money. Beginners can get a feel for the market’s ebb and flow, experiment with different trading instruments, and understand the mechanics of trades without the emotional stress associated with real losses.
Testing Trading Strategies
Practice accounts allow for the testing of trading strategies in real-time market conditions. This hands-on experience is crucial for understanding how different strategies perform under various market scenarios, helping traders refine their approaches based on empirical evidence.
Familiarization with Trading Platforms
Demo accounts provide an opportunity to become acquainted with trading platforms’ interfaces and functionalities. Mastery of these tools is essential for efficient trading, as it enables quick decision-making and execution of trades.
Understanding Market Movements
Engaging with the market through a practice account helps in developing an intuition for market trends and price movements. This practical insight is invaluable and can only be gained through experience.

How to Effectively Use Practice Accounts
Treat It Like Real Money
To maximize the learning experience, treat the virtual money in your demo account as if it were real. This approach fosters discipline and realistic trading habits, making the transition to live trading smoother and more successful.
Set Realistic Goals
Define clear, achievable goals for your practice trading. Whether it’s testing a particular strategy, getting familiar with the trading platform, or understanding certain market conditions, having specific objectives can guide your learning process effectively.
Keep a Trading Journal
Documenting your trades, including the strategy used, market conditions, outcomes, and your emotional state, can offer valuable insights. Reviewing this journal can help identify successful patterns and areas needing improvement.
Limit Your Practice Time
While demo accounts are beneficial, spending too much time in a risk-free environment can lead to complacency. Set a timeline for your practice trading, after which you should evaluate your readiness for real trading. Typically, a few months should suffice to gain basic proficiency.
Use Realistic Amounts of Virtual Capital
Practicing with an amount of virtual capital similar to what you plan to invest in real trading can provide a more accurate representation of potential gains and losses. This realism helps set appropriate expectations for live trading performance.
Explore Different Markets and Instruments
Use the opportunity to explore various markets (stocks, forex, commodities) and instruments (CFDs, options). This exploration can help diversify your trading skills and identify areas where you might be more comfortable or successful.

Executing Your First Stock Trade
Making your first stock trade is a significant step in your journey as an investor. This detailed guide aims to navigate the process of buying and selling stocks for beginners, emphasizing common pitfalls to avoid and ensuring a smooth initiation into the world of stock trading.
Step-by-Step Guide to Buying Stocks
Step 1: Research and Select a Stock
Begin with thorough research to identify stocks that align with your investment goals and risk tolerance. Consider factors such as the company’s financial health, industry trends, and market conditions. Utilize financial news, analyst reports, and company earnings statements as part of your research.
Step 2: Choose a Brokerage Account
Select a brokerage account that suits your needs, based on factors like commission fees, platform usability, and available educational resources. Ensure the broker is reputable and regulated by financial authorities.
Step 3: Fund Your Account
Deposit funds into your brokerage account. Be mindful of the settlement period, which is the time it takes for your funds to become available for trading.
Step 4: Use a Trading Platform
Familiarize yourself with the trading platform provided by your broker. Understand how to navigate it, access market data, and use tools available for analysis.
Step 5: Place Your Order
Decide on the number of shares you want to buy and the type of order you wish to place. The most common types are:
- Market Order: Buys the stock immediately at the current market price.
- Limit Order: Sets a specific price at which you want to buy the stock. The trade only executes if the stock reaches this price.
Review your order, ensuring all details are correct before submission.
Step 6: Monitor Your Investment
After purchasing, monitor your investment’s performance, keeping an eye on company news and market trends that may affect stock value.
Step-by-Step Guide to Selling Stocks
Step 1: Evaluate Your Position
Regularly review your portfolio to decide whether it’s time to sell a stock. This decision can be based on achieving a target return, changing financial goals, or deteriorating fundamentals of the invested company.
Step 2: Choose the Type of Sell Order
Similar to buying, decide if you want to place a market or limit order. If aiming for a specific return, a limit order might be more appropriate.
Step 3: Execute the Sell Order
Through your trading platform, select the stock you wish to sell, enter the number of shares, choose your order type, and place the sell order. Always double-check the details before confirming.

Common Mistakes to Avoid for finding Best stock brokers
- Acting on Emotions: Avoid making impulsive decisions based on fear or greed. Stick to your investment strategy and make rational choices.
- Ignoring Transaction Costs: Be aware of commission fees and taxes, as they can eat into your profits. Consider these costs when making buy or sell decisions.
- Overtrading: Frequent buying and selling can lead to high transaction costs and taxes, potentially diminishing returns.
- Failing to Diversify: Don’t put all your money into a single stock. Diversification can reduce risk by spreading investments across various sectors or asset classes.
- Neglecting Research: Always base your investment decisions on thorough research rather than following market trends or tips from unverified sources.
Selecting Your First Stock Broker: A Comprehensive Guide
Choosing the right stock broker is a pivotal decision for every beginner investor. The broker acts as a gateway to the markets, offering trading platforms, tools, resources, and support necessary for navigating the world of stock trading. This guide outlines the essential steps for evaluating and selecting a broker that aligns with your investment goals and preferences, followed by recommendations for beginner-friendly stock brokers based on detailed analysis.
Steps for Evaluating and Choosing the Best stock brokers
Step 1: Determine Your Investment Goals
Identify your investment objectives, whether it’s long-term growth, income through dividends, or active trading. Your goals will influence the type of broker that best suits your needs.
Step 2: Consider the Types of Investments You’re Interested In
Different brokers offer access to various markets and investment products. Ensure the broker supports the assets you’re interested in, such as stocks, bonds, ETFs, mutual funds, or options.
Step 3: Evaluate the Broker’s Fees and Commission Structure
Compare the fee structures of potential brokers, including commission rates for trades, account maintenance fees, and any other associated costs. Look for transparency in pricing to avoid unexpected charges.
Step 4: Assess the Trading Platform and Technology
The trading platform is your primary tool for managing investments. Look for platforms that are user-friendly yet offer powerful tools for analysis, research, and executing trades. Many brokers offer demo accounts to test their platforms.
Step 5: Check for Educational Resources and Support
For beginners, educational materials, tutorials, webinars, and responsive customer support are invaluable. Evaluate the quality and accessibility of the broker’s educational content and the availability of support via phone, email, and live chat.
Step 6: Review the Broker’s Reputation and Regulatory Compliance
Ensure the broker is regulated by reputable authorities, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in the U.S. or the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK. Check for any history of regulatory violations or customer complaints.
Step 7: Consider Additional Features and Services
Some brokers offer extra services like robo-advisors, social trading platforms, or advanced charting tools. While not essential for everyone, these features may enhance your trading experience.

Recommended Beginner-Friendly Best stock brokers
E*TRADE
- Pros: Comprehensive educational resources, user-friendly platforms, and extensive research tools make E*TRADE ideal for beginners. Offers $0 commission trades on U.S. stocks and ETFs.
- Cons: Higher fees for active traders or advanced trading features.
TD Ameritrade
- Pros: Offers a wide range of investments, superior research tools, and excellent customer support. The Thinkorswim platform is highly regarded for trading and analysis.
- Cons: May be overwhelming for absolute beginners due to the depth of features.
Robinhood
- Pros: Known for its simple, intuitive app and commission-free trades. Robinhood is attractive for beginners interested in a straightforward trading experience.
- Cons: Limited investment products and research tools compared to other brokers.
Fidelity
- Pros: Offers $0 commission trades, extensive research resources, and advanced tools through its Active Trader Pro platform. Notable for its customer service and investor education.
- Cons: Some advanced features may require meeting certain account minimums.

FAQs:
- What Is Stock Trading?
- Trading stocks involves buying and selling shares of companies to profit from price fluctuations.
- Why is Choosing the Right Broker Important for Beginners?
- The right broker provides the tools, resources, and support necessary for learning and successful trading.
- How Do Broker Fees Affect Stock Trading?
- Fees can eat into profits, especially for active traders, making it crucial to understand and manage them.
- What Are the Key Regulations Governing Stock Brokers?
- Agencies like the SEC and FINRA regulate brokers to ensure transparency and protect investor interests.
- Can I Start Trading Stocks with a Small Investment?
- Yes, many brokers offer accounts with low or no minimum deposit requirements, making it accessible to start small.
- How Do I Open a Stock Trading Account?
- Select a broker, complete their application process, provide any necessary documentation, and fund your account.
- What is a Demo Account, and Should I Use One?
- A demo or paper trading account lets you practice trading with virtual money, invaluable for learning without risk.
- What Should I Look for in a Trading Platform?
- Look for platforms with intuitive interfaces, robust educational resources, and strong customer support tailored to beginners.
- How Can I Ensure a Broker is Reliable?
- Verify their regulatory compliance, review user feedback, and assess their trading conditions and support services.
- When Should I Transition from Practice to Real Trading?
- After gaining confidence in your trading strategy and understanding the market, consider moving to real trading with a cautious approach to risk management.
This guide structure and FAQs are designed to demystify the process of selecting a stock broker for beginners, providing them with the knowledge needed to start their trading journey on solid ground.

