CMC Markets Products is a globally recognized trading platform known for its robust trading tools, extensive range of financial products, and comprehensive educational resources. Established in 1989, CMC Markets has grown to become one of the leading providers of online financial trading, serving retail and institutional investors alike. Here’s an overview of the platform and a summary of the types of financial products it offers.
Overview of CMC Markets as a Global Trading Platform
Global Reach and Regulation
- Global Presence: CMC Markets operates in multiple countries across the globe, providing services to over 60,000 clients worldwide.
- Regulatory Compliance: It is regulated by several top-tier authorities, including the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK, ensuring a high standard of governance and transparency.
Trading Technology
- Advanced Trading Platforms: CMC Markets offers a proprietary trading platform known as ‘Next Generation Platform’ alongside the popular MetaTrader 4 (MT4). These platforms are equipped with advanced charting tools, automated trading capabilities, and customizable interfaces.
- Mobile Trading: Comprehensive mobile apps that mirror the functionality of desktop platforms, providing traders with the flexibility to trade on the go.
Customer Support and Education
- Customer Support: CMC Markets provides multi-lingual customer support via phone, email, and live chat, ensuring that traders can receive assistance whenever needed.
- Educational Resources: A wealth of educational materials, including webinars, tutorials, e-books, and articles, which cater to both novice traders and experienced professionals.
Summary of Financial CMC Markets Products Available
Forex Trading
- Currency Pairs: Offers a wide range of major, minor, and exotic currency pairs, allowing traders to take advantage of fluctuations in global forex markets.
CFD Trading
- Stocks and Indices: Traders can speculate on the price movements of individual stocks or major global indices without the need to own the underlying assets.
- Commodities: Includes trading on various commodities such as gold, silver, oil, and more, providing traders with opportunities to diversify their portfolios.
- Treasuries: Ability to trade on government securities such as bonds and gilts, appealing to those looking for lower-risk investment options.
Cryptocurrencies
- Digital Currencies: Offers trading on major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others, catering to the growing demand for digital currency investments.
Other Products
- ETFs and ETCs: Traders can also invest in Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and Exchange-Traded Commodities (ETCs), which track the performance of indexes or commodities.
Unique Features
- Risk Management Tools: Includes features like stop-loss orders, guaranteed stop-loss orders, and price alerts to help traders manage their risks effectively.
- Research and Analysis Tools: Provides advanced technical analysis tools and up-to-date market insights that assist traders in making informed decisions.
CMC Markets stands out for its comprehensive range of trading options, cutting-edge technology, and strong regulatory framework, making it a preferred choice for traders seeking a reliable and diverse trading environment. Whether you are new to trading or an experienced trader looking for robust trading capabilities, CMC Markets offers the tools and resources necessary to support your trading journey.
Forex Trading on CMC Markets Products
CMC Markets is a renowned global platform that offers extensive opportunities for Forex trading. With a broad range of available currency pairs—from majors and minors to exotics—traders can engage in various Forex trading strategies to capitalize on fluctuations in the global currency markets. Here’s a detailed look at the Forex trading options available on CMC Markets and some essential tips and strategies for effective trading.
Available Currency Pairs
Major Currency Pairs
- Examples: EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, USD/CHF, AUD/USD, USD/CAD, NZD/USD.
- Characteristics: These pairs are the most traded in the world, representing the world’s largest economies. They offer high liquidity, lower spreads, and tend to be less volatile than minor and exotic pairs.
Minor Currency Pairs
- Examples: EUR/GBP, EUR/AUD, GBP/JPY, CHF/JPY, NZD/JPY.
- Characteristics: These pairs do not include the US dollar but involve other major currencies. They are less liquid than the major pairs and can exhibit higher volatility and wider spreads.
Exotic Currency Pairs
- Examples: EUR/TRY, USD/SGD, GBP/ZAR, JPY/NOK.
- Characteristics: Exotic pairs include one major currency and one from a smaller or emerging economy. These pairs are less liquid, more volatile, and have wider spreads, but they can offer significant opportunities for the astute trader.
Tips and Strategies for Forex Trading on CMC Markets
Fundamental Analysis
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of global economic news and events that can affect currency markets. Economic indicators, interest rate decisions, and political events can significantly impact currency prices.
- Economic Calendars: Utilize economic calendars to track upcoming events and prepare for potential market movements.
Technical Analysis
- Charting Tools: Use CMC Markets’ advanced charting tools to analyze market trends. Look for support and resistance levels, chart patterns, and use technical indicators to gauge market sentiment.
- Multi-Timeframe Analysis: Analyze currency pairs across different timeframes to get a broader perspective on the market trend.
Risk Management
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Consider using guaranteed stop-loss orders available on CMC Markets to protect against market gaps.
- Manage Leverage: Use leverage cautiously. While it can amplify profits, it can also increase losses. Adjust leverage based on your risk tolerance and trading strategy.
Trading Psychology
- Maintain Discipline: Develop a trading plan and stick to it. Avoid making impulsive decisions based on emotions.
- Continuous Learning: The Forex market is dynamic. Continuously educate yourself on market trends, new strategies, and financial news.
Trading Plan and Strategy
- Develop a Trading Plan: Define your financial goals, risk tolerance, and strategies. Your trading plan should include how you will enter and exit trades, trading times, and expected frequency of trades.
- Review and Adjust: Regularly review your trades and overall strategy to adapt to changing market conditions and improve your trading performance.
Use of Technology
- Mobile Trading: Take advantage of CMC Markets’ mobile trading apps to trade on the go and stay updated with real-time market data.
Commodities Trading Overview
Commodities trading involves buying and selling products that are either extracted from the ground (metals, energy) or grown (agricultural products). These trades can be executed on futures exchanges, which allow traders to buy and sell contracts based on the future delivery of these physical goods. Trading commodities can diversify a trader’s portfolio beyond traditional securities like stocks and bonds. Here’s an explanation of the different types of commodities, how to trade them, and the factors affecting their prices.
Types of Commodities
Metals
- Precious Metals: These include gold, silver, and platinum. Precious metals are often used as a hedge against inflation and currency devaluation.
- Industrial Metals: Examples include copper, nickel, and aluminum. Prices can be highly sensitive to changes in economic growth as they are widely used in construction and manufacturing.
Energy
- Crude Oil: One of the most traded commodities due to its significant role in the global economy. Variants include WTI (West Texas Intermediate) and Brent crude.
- Natural Gas: Often influenced by geographical and seasonal factors that can affect supply and demand.
- Other Energy Commodities: Include coal and uranium, which have their own specific market dynamics.
Agricultural CMC Markets Products
- Grains: Such as wheat, corn, and soybeans. These are staple foods around the world and can be highly volatile during growing seasons.
- Soft Commodities: Include coffee, sugar, and cotton. Prices can be affected by factors ranging from weather conditions to changes in consumer taste.
How to Trade Commodities
Futures Contracts
Commodities are primarily traded through futures contracts on exchanges like the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME) and Intercontinental Exchange (ICE). A futures contract is an agreement to buy or sell a particular commodity at a predetermined price at a specified time in the future.
Spot Trading
For some commodities, particularly precious metals, spot trading is also common. This involves the direct trading of commodities for immediate delivery.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and Stocks
Investors can also trade commodities through ETFs that track commodity prices or stocks of companies involved in commodities, such as mining or energy firms.
Factors Affecting Commodity Prices
Economic Indicators
- Supply and Demand: Basic economic factors like supply and demand are primary price drivers. For example, a poor harvest due to drought will decrease the supply of agricultural CMC Markets Products, pushing prices up.
- Economic Growth: Industrial commodities, such as oil and copper, often depend on global economic conditions. High economic growth can increase demand for these commodities.
Geopolitical Factors
- Political Stability: Commodity prices can be influenced by political stability in countries that supply these commodities. For example, oil prices can fluctuate wildly based on Middle Eastern political conditions.
- Trade Policies: Tariffs and other trade barriers can affect commodity prices by altering the flow of goods and changing supply-demand dynamics.
Environmental Conditions
- Weather: Weather plays a crucial role in the pricing of agricultural commodities. Unexpected changes in weather conditions can significantly affect crop yields.
- Natural Disasters: Earthquakes, hurricanes, and other disasters can disrupt production and supply chains, leading to price volatility.
Market Sentiment
- Investor Sentiment: Commodities can also be affected by speculative investments where traders react to market news and sentiment rather than fundamental supply and demand.
Trading Strategy Tips
- Stay Informed: Keep up with global news and reports that may affect commodity prices.
- Use Technical Analysis: Many commodity traders use technical analysis to identify trends and potential reversal points in the market.
- Manage Risk: Employ risk management techniques, such as stop-loss orders, to protect against market volatility.
Commodities trading offers a unique opportunity to profit from changes in global economic conditions. Whether trading directly through futures and spot markets or indirectly through ETFs and stocks, understanding the underlying factors that affect commodity prices can enhance your trading strategies and potential returns.

Indices Trading on CMC Markets
Trading indices offers investors exposure to entire sectors or economies at once, rather than selecting individual stocks. CMC Markets provides access to a range of global indices, allowing traders to speculate on the movements of major stock markets around the world. Here, we will explore the list of global indices available on CMC Markets and provide a guide to trading indices effectively.
List of Global Indices Available on CMC Markets
CMC Markets offers a broad selection of indices from major global markets, ensuring traders can find indices that best match their trading strategy and focus. Some of the key indices include:
Major Global Indices
- US Indices:
- Dow Jones Industrial Average (US30)
- S&P 500 (US500)
- NASDAQ Composite (US100)
- European Indices:
- FTSE 100 (UK100) — United Kingdom
- DAX (GER30) — Germany
- CAC 40 (FRA40) — France
- Asian Indices:
- Nikkei 225 (JPN225) — Japan
- Hang Seng Index (HK50) — Hong Kong
- ASX 200 (AUS200) — Australia
Emerging Market Indices
- Brazil Bovespa (BRA50)
- Russia MOEX (RUS50)
- India Nifty 50 (IND50)
These indices cover a wide range of the global economy, providing ample trading opportunities for both regional market trends and global economic shifts.
Guide to Trading Indices
Understanding Index Composition
- Diverse Exposure: Each index is composed of a set of companies, often representing a broad market or a specific sector. Understanding the composition of an index is crucial as it helps predict how different economic, political, or corporate events might affect the index.
- Sector Weighting: Some indices may be heavily weighted towards particular sectors (e.g., NASDAQ is tech-heavy). Movements in these sectors can disproportionately influence the index.
Analyzing Market Movements
- Economic Indicators: Data such as GDP growth, employment rates, and inflation can impact indices as they reflect the economic health that supports the companies within the index.
- Political Events: Elections, regulatory changes, and trade policies can cause fluctuations in indices, especially if they significantly impact business conditions.
- Global Events: Worldwide events like pandemics or financial crises can cause markets to fluctuate sharply and unpredictably.
Trading Strategies
- Trend Following: This strategy involves identifying the direction of the market trend and trading in alignment with it. Technical indicators like moving averages can help identify trends.
- Swing Trading: This involves taking trades that capture the ‘swing’ movements in market prices. Swing traders can benefit from volatility by capturing short-term upward and downward movements.
- Day Trading: Indices are popular among day traders due to their liquidity and large range of intraday movements. This strategy requires close monitoring of short-term price movements throughout the trading day.
Risk Management
- Stop-Loss Orders: Always use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. This is crucial in indices trading, where leverage can amplify both gains and losses.
- Diversification: Although trading an index inherently provides diversification, consider diversifying across different indices and asset classes to spread risk further.
- Stay Informed: Keeping up-to-date with market news and events is vital for timely decision-making in index trading.
Use of Technology
- Technical Analysis Tools: Utilize CMC Markets’ advanced charting tools to analyze historical price movements and forecast future trends.
- Economic Calendars: Use economic calendars to stay ahead of market-moving events, helping you plan your trades more effectively.
Shares and ETFs on CMC Markets
Trading shares and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) on CMC Markets provides traders with opportunities to participate in the equity markets without directly purchasing stocks or assets. This guide provides an overview of the options available for stock and ETF trading on CMC Markets and discusses the benefits of using this platform for these types of investments.
Overview of Stock Trading on CMC Markets
CMC Markets offers its clients the ability to trade individual stocks across major global exchanges. This includes markets in the United States, Europe, and Asia, allowing traders to gain exposure to different economic regions and industries.
Available Stock Markets
- United States: Includes major companies listed on the NYSE and NASDAQ.
- Europe: Features top companies from the UK (FTSE), Germany (DAX), and other European exchanges.
- Asia-Pacific: Offers stocks from exchanges in Australia (ASX), Japan (Nikkei), and more.
Traders can choose from a wide range of sectors such as technology, finance, healthcare, and consumer goods, making it possible to diversify their trading strategies according to market conditions and personal investment goals.
Overview of ETFs on CMC Markets
CMC Markets provides access to a variety of ETFs, which are funds that track indices, commodities, or baskets of assets like an index fund but trade like a stock on an exchange. ETFs offer a cost-effective way to diversify portfolios without the need to manage individual assets.
Types of ETFs Available
- Index ETFs: Track major indices such as the S&P 500, NASDAQ, or international indices.
- Commodity ETFs: Provide exposure to physical goods such as gold, oil, or agricultural CMC Markets Products.
- Sector ETFs: Target specific sectors of the economy, such as technology, energy, or healthcare.
- Thematic ETFs: Focus on specific investment themes, like green energy or emerging technologies.
Benefits of Trading Shares and ETFs through CMC Markets
Broad Access
- Global Reach: Traders can access a vast array of stocks and ETFs from around the world, all from one trading platform.
- Diverse Options: Offers opportunities to invest in various sectors and themes, catering to different risk appetites and investment strategies.
Advanced Trading Tools
- Research and Analysis: CMC Markets provides comprehensive market analysis and research tools that help traders make informed decisions. This includes access to up-to-date news, economic data, and expert commentary.
- Charting Tools: Advanced charting capabilities allow traders to perform technical analysis using a variety of indicators and chart patterns.
Cost Efficiency
- Competitive Spreads: CMC Markets offers competitive spreads on shares and ETFs, which can help reduce trading costs.
- No Stamp Duty: Trading shares through CFDs on CMC Markets means traders can avoid stamp duty (a tax on document transactions in stock exchanges), which is charged in some markets like the UK.
Flexibility and Convenience
- Trading on Margin: Offers the ability to trade on margin, providing the potential for significant returns (though also increasing potential risks).
- Seamless Platform Integration: Both stocks and ETFs can be traded via CMC Markets’ mobile app or desktop platform, allowing for seamless trading and portfolio management on the go.
Risk Management Features
- Stop-Loss Orders: Traders can use stop-loss orders to manage and mitigate their risks effectively.
- Hedging Capabilities: Allows traders to hedge their positions by going long or short using CFDs, providing a strategy to potentially offset losses in volatile markets.
Trading shares and ETFs through CMC Markets can be a strategic choice for those looking to diversify their investment portfolios or take advantage of movements in the global markets. With its advanced tools, diverse offerings, and robust platform, CMC Markets caters to both novice investors and experienced traders looking to expand their trading horizons.

Cryptocurrency Trading on CMC Markets
Cryptocurrency trading has become a dynamic and integral part of the global financial landscape, offering new opportunities for traders. CMC Markets provides a platform for trading various cryptocurrencies, combining the traditional trading environment with access to the burgeoning digital currency market. This guide explores cryptocurrency trading on CMC Markets, discussing both the risks and rewards associated with this type of trading.
Introduction to Cryptocurrency Trading on CMC Markets
CMC Markets offers trading in several major cryptocurrencies as CFDs (Contracts for Difference), allowing traders to speculate on the price movements of cryptocurrencies without the need to own the actual digital coins.
Available Cryptocurrencies
- Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most widely recognized cryptocurrency.
- Ethereum (ETH): Known for its smart contract functionality.
- Ripple (XRP): Popular for its digital payment protocol more than its cryptocurrency.
- Litecoin (LTC) and Bitcoin Cash (BCH): Considered as alternatives to Bitcoin, with variations in block generation time and other technical details.
These cryptocurrencies can be traded against major fiat currencies such as the USD, EUR, and GBP, providing a variety of trading pairs for CMC Markets clients.
Risks of Trading Cryptocurrencies
Volatility
- Cryptocurrencies are notoriously volatile, with prices capable of substantial movements within a short period. This volatility can lead to significant profits but also substantial losses.
Market Hours
- Cryptocurrency markets operate 24/7, which means trading opportunities are constant, but this can also make it challenging to manage trades and risks effectively without constant monitoring.
Regulatory Changes
- The cryptocurrency market is subject to evolving regulatory considerations that can impact prices dramatically. Changes in how countries regulate cryptocurrencies, such as Japan or South Korea, can influence market prices globally.
Technological Risks
- Unlike traditional currencies, cryptocurrencies are entirely digital and dependent on technology, making them susceptible to cybersecurity risks, including hacking.
Rewards of Trading Cryptocurrencies
High Liquidity
- Cryptocurrency markets are highly liquid, especially for major coins like Bitcoin and Ethereum, which means large trades can be executed without significantly affecting the market price.
Potential for High Returns
- The high volatility of cryptocurrencies, while risky, also presents opportunities for substantial returns, especially for day traders and those who can manage the rapid price changes effectively.
Diversification
- Adding cryptocurrencies to a diversified trading portfolio can spread risk across various asset classes, potentially increasing returns while lowering the overall risk.
Accessibility
- Cryptocurrencies eliminate many traditional barriers to entry in financial markets, making it easier for a broader audience to participate in trading.
Trading Strategies and Best Practices
Technical Analysis
- Utilize technical analysis tools provided by CMC Markets to identify trends, support, and resistance levels. Cryptocurrencies often follow market patterns that can be predicted with various analytical tools.
Risk Management
- Employ strict risk management techniques, such as stop-loss and take-profit orders, to protect your investments, especially given the volatile nature of cryptocurrency markets.
Stay Informed
- Keep up-to-date with the latest cryptocurrency news and developments. The market sentiment can drastically change due to news events, impacting prices immediately.
Use a Demo Account
- Before diving into cryptocurrency trading, practice with a demo account offered by CMC Markets. This can help you understand market behavior without any financial risk.
Cryptocurrency trading on CMC Markets provides an exciting opportunity to engage with the fast-paced digital currency market. By understanding the risks and rewards and employing careful trading strategies, traders can potentially reap significant benefits from this innovative market.
Bonds and Interest Rate CMC Markets Products
Trading bonds and interest rate products is a crucial aspect of the financial markets, offering investors the potential for income, diversification, and risk management. This discussion will explore the types of bond products available on CMC Markets Products, as well as strategies for trading these instruments effectively.
Availability and Types of Bond CMC Markets Products
CMC Markets provides access to a variety of bond and interest rate products, allowing traders to speculate on or hedge against changes in interest rates and credit markets. Here are the common types of bond products offered:
Government Bonds
- Treasuries: These include U.S. Treasury bonds, which are considered among the safest investments since they are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government.
- Gilts: UK government bonds, known as Gilts, offer a similar risk profile to U.S. Treasuries.
- Bunds: German government bonds, or Bunds, are crucial for Eurozone interest rate trading.
Corporate Bonds
- While less common on retail platforms like CMC Markets, some platforms may offer ETFs or CFDs that track the performance of corporate bonds, providing exposure to corporate debt markets.
Interest Rate CMC Markets Products
- Futures and Options: CMC Markets Products based on interest rates, such as Euribor, Short Sterling, and U.S. T-Bills. These derivatives are used to trade expectations on the direction of interest rates.
Strategies for Trading Bonds and Interest Rates
Fundamental Analysis
- Economic Indicators: Monitor key economic reports, such as inflation rates, employment figures, and GDP growth, as these can significantly affect bond prices and interest rates.
- Monetary Policy: Decisions by central banks on interest rates are pivotal. For example, a rate hike typically leads to lower bond prices, while rate cuts might boost them.
- Market Sentiment: In times of uncertainty, there might be a ‘flight to quality’ where investors flock to government bonds, driving prices up.
Technical Analysis
- Trend Lines and Moving Averages: Use these tools to determine trends in bond prices or interest rate movements.
- Volume and Oscillators: Analyze trading volume and momentum indicators to assess the strength of price movements and potential reversals.
Hedging Interest Rate Exposure
- Interest Rate Swaps and Futures: Utilize these derivatives to hedge against interest rate risks, especially if managing a portfolio with significant interest rate exposure.
- Diversification: Incorporate a mix of bonds with varying maturities and credit qualities to reduce risk.
Yield Curve Analysis
- Curve Positioning: Understanding the shape of the yield curve (normal, inverted, steep, flat) can provide insights into economic expectations and potential trading strategies.
- Carry Trades: In stable rate environments, buying high-yield bonds and selling lower-yield bonds (carry trading) can be profitable, albeit with higher risk.
Timing and Liquidity
- Trading Hours: Bond markets have specific hours that can influence liquidity and spreads. Knowing these can help in planning entry and exit points.
- Event-Driven Strategies: Position before significant economic events or central bank meetings to capitalize on expected movements in interest rates or bond prices.
Risk Management
- Stop-Loss Orders: Given the potential for sudden market moves due to policy changes or economic reports, using stop-loss orders can help limit losses.
- Portfolio Diversification: Beyond different types of bonds, consider diversifying across other asset classes to manage overall portfolio risk.

Treasury CMC Markets Products Overview
Treasury products, including T-Bills and other government securities, are fundamental components of the financial markets. These CMC Markets Products offer investors a relatively safe investment compared to stocks and other higher-risk assets. Understanding these instruments and how to incorporate them into a diversified trading strategy can help manage risk and stabilize returns.
Details on Treasury CMC Markets Products
T-Bills (Treasury Bills)
- Description: T-Bills are short-term government securities that mature in one year or less. They are sold at a discount to their face value, and at maturity, the government pays the T-Bill’s full face value. The difference represents the investor’s earnings.
- Risk Profile: T-Bills are considered one of the safest investments as they are backed by the full faith and credit of the issuing government, typically involving very low risk of default.
Treasury Notes and Bonds
- Treasury Notes: These are medium-term securities issued by the government, with maturities ranging from one to ten years. They pay interest every six months.
- Treasury Bonds: Long-term securities, with maturities extending beyond ten years up to thirty years. Like notes, they pay interest semi-annually.
Government Securities
- Features: Governments issue various securities to finance their debt, including fixed-rate bonds, inflation-indexed bonds, and savings bonds. These can vary widely in terms of duration, interest payments, and risk profile.
- Global Variants: Besides U.S. Treasuries, other countries issue similar instruments, such as UK Gilts, German Bunds, and Japanese Government Bonds (JGBs).
Incorporating Treasury CMC Markets Products into a Diversified Trading Strategy
Risk Management
- Safe Haven: Treasury products are considered safe-haven assets, often sought after in times of market uncertainty or high volatility. They can serve as a hedge against downturns in riskier asset classes like stocks.
- Low Correlation: Incorporating T-Bills and other government securities can lower the overall portfolio volatility because their price movements are generally less correlated with those of equities.
Income Generation
- Regular Income: Treasury Notes and Bonds provide regular interest payments, which can offer a steady income stream for investors, contributing positively to cash flow.
- Predictability: The fixed income from these securities can be particularly appealing during periods of low interest rates or when other income-generating investments might offer lower yields.
Strategic Allocation
- Laddering Strategy: By purchasing T-Bills, Notes, or Bonds with varying maturities (a technique known as “laddering”), investors can manage liquidity needs and interest rate risks more effectively, taking advantage of different interest environments over time.
- Duration Matching: Investors can use the duration of Treasury products to match the liability or goal horizons, ensuring that capital is available when needed without significant risk of loss.
Diversification
- Global Diversification: Including government securities from different countries can help diversify geopolitical risks and take advantage of varying economic cycles and interest rates globally.
- Asset Allocation: Treasuries should be part of a broader asset allocation strategy that includes stocks, bonds, and possibly alternative investments, balancing the risk and return according to individual investment goals.
Tactical Moves
- Market Timing: While generally not advisable as a core strategy, tactical shifts in the weighting of Treasury products in a portfolio can capitalize on expected movements in interest rates or economic conditions.
Monitoring and Adjustment
- Regular Review: The effectiveness of including Treasury products in a portfolio should be regularly reviewed and rebalanced in response to changes in market conditions, interest rates, and personal financial objectives.
CFDs and Spread Betting: Explanation, Differences, and Risks
Contracts for Difference (CFDs) and spread betting are two popular forms of derivative trading that allow traders to speculate on financial markets without owning the underlying assets. Both methods offer potential benefits but come with significant risks and are best suited to experienced traders. Here’s an in-depth look at each, highlighting their differences and associated risks.
What are CFDs?
CFDs are agreements between a trader and a broker to exchange the difference in the price of an asset from the time the contract is opened to when it is closed. The trader aims to profit from price movements without actually owning the underlying asset.
Key Features of CFD Trading:
- Leverage: CFDs provide the ability to trade on margin, meaning traders can open larger positions than their capital would otherwise allow.
- Market Access: Traders can speculate on the rising and falling prices of rapidly moving global financial markets (e.g., stocks, forex, commodities, indices).
- Ownership: No ownership of the underlying asset; the contract is purely speculative.
What is Spread Betting?
Spread Betting is a derivative strategy where traders bet on the direction in which an asset’s price will move. It is similar to CFDs but is tax-free in some jurisdictions like the UK.
Key Features of Spread Betting:
- Tax Efficiency: In the UK, spread betting is free from capital gains tax and stamp duty.
- Betting Units: Traders bet an amount per point of movement in the underlying asset.
- Market Range: Includes a wide range of markets, from forex to shares and commodities.
Differences Between CFDs and Spread Betting
| Aspect | CFD Trading | Spread Betting |
|——–|————-|—————-|
| Tax | Profits may be subject to capital gains tax. | No capital gains tax on profits (UK). |
| Market Access | Global markets | Primarily UK and Ireland; some global markets. |
| Trading Costs | Commission fees and financing charges may apply. | Costs built into the spread; no direct commissions. |
| Profit Calculation | Based on the number of contracts and the difference in price. | Based on the stake per point and the number of points moved. |
| Regulation | Heavily regulated globally. | Regulated mainly in the UK. |
Risks Associated with CFDs and Spread Betting
Leverage Risk
- High leverage in both CFDs and spread betting amplifies both gains and losses, which can exceed deposits.
Market Volatility
- Price Fluctuations can result in rapid losses, especially if stop-loss orders are not effectively used.
Overtrading
- Ease of Market Access and low initial capital requirements can lead to overtrading, impacting financial stability.
Regulatory Risk
- Legal and Tax Implications vary by region and can affect the profitability and legality of strategies.
How to Use CFDs and Spread Betting to Leverage Market Positions
Strategic Planning
- Define Goals and Risk Tolerance: Understand your financial goals and how much risk you can assume in your trading strategies.
Utilize Technical and Fundamental Analysis
- Market Research: Use both analyses to predict price movements and inform your trading decisions.
Implement Risk Management
- Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders: Essential for managing risks in volatile trading conditions.
- Diversify: Spread your capital across different markets to reduce risk.
Monitor and Adjust
- Stay Informed: Keep abreast of market conditions, economic indicators, and geopolitical events that could affect your positions.
- Review and Adapt: Regularly assess your strategies and adjust them based on performance and market dynamics.
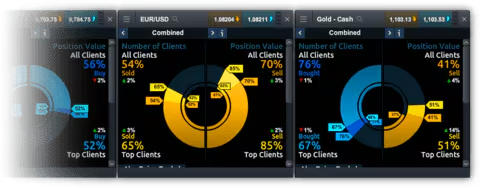
Advanced Trading Tools and Features on CMC Markets
CMC Markets offers a range of advanced trading tools and features designed to enhance trading effectiveness and efficiency. These tools cater to both novice and experienced traders, providing deep market insights, facilitating complex strategy execution, and improving risk management. Below, we explore some of these advanced tools available on CMC Markets and how traders can utilize them to optimize their trading activities.
Key Advanced Trading Tools and Features on CMC Markets
1. Next Generation Trading Platform
- Customizable Layouts: Users can tailor their trading dashboard according to their preferences, focusing on the information that matters most to them.
- Advanced Charting Package: Comes with over 115 technical indicators and drawing tools, customizable chart types, and a pattern recognition scanner to help traders identify trading opportunities based on technical setups.
2. Mobile Trading App
- Seamless Integration: Offers full functionality across mobile devices, ensuring traders can manage and execute trades anytime, anywhere.
- Mobile-Optimized Tools: Includes mobile-friendly charting tools, live price alerts, and the ability to trade directly from charts.
3. Client Sentiment Tool
- Market Sentiment Data: Displays the percentage of CMC Markets clients who have bought versus those who have sold on a particular CMC Markets Products, giving traders insight into market sentiment.
- Application: Use this tool to gauge whether a market is overbought or oversold, potentially indicating a reversal or continuation of the current trend.
4. Price Projection Tool
- Functionality: Allows traders to visually set entry and exit points on charts, projecting potential profit or loss scenarios.
- Usage: Enhance decision-making by mapping out possible future price movements based on historical data and current market conditions.
5. Guaranteed Stop-Loss Orders (GSLO)
- Risk Management: Guarantees to close your trade at the specified price without any slippage, even during volatile market conditions.
- Strategic Use: Ideal for limiting downside risk, particularly in volatile markets or for positions held open during news events.
6. Economic Calendar
- Tracking Events: Provides traders with schedules of important economic announcements that can affect markets, like GDP announcements, interest rate decisions, and employment figures.
- Planning Trades: Use this calendar to plan trades around major economic events, potentially avoiding trading during high volatility or targeting opportunities triggered by news.
7. Module Linking
- Efficient Workflow: Link different modules so that changing the CMC Markets Products in one module automatically updates all linked modules (e.g., charts, order tickets, analysis).
- Enhanced Coordination: Keeps your analysis and trades synchronized, saving time and reducing errors in fast-moving markets.

How to Use Platform Features to Enhance Trading Effectiveness
Implement Comprehensive Market Analysis
- Utilize the advanced charting tools and technical indicators to perform detailed market analysis. Combine these tools with fundamental insights from the economic calendar and client sentiment to develop a well-rounded market perspective.
Employ Tactical Trade Management
- Use the price projection tool to visualize potential trade outcomes before execution. Combine this with GSLOs to manage risk effectively, particularly in uncertain or volatile market conditions.
Stay Informed and Responsive
- Regularly consult the economic calendar and set up alerts for upcoming financial events to stay ahead of market movements. Use mobile trading capabilities to maintain control of your trades and react promptly to market changes, even when away from your desk.
Continuously Optimize Strategies
- Regularly review trading strategies based on performance data and insights gathered from the platform’s analysis tools. Adjust strategies as needed to align with changing market conditions and trading goals.
By leveraging these advanced tools and features offered by CMC Markets, traders can enhance their trading effectiveness, manage risks more efficiently, and potentially increase their trading success over time.
Risk Management and Compliance on CMC Markets
Effective risk management and adherence to compliance and regulatory standards are crucial for successful trading on platforms like CMC Markets. Understanding and implementing sound risk management techniques not only protect investments but also ensure trading activities are conducted within legal and ethical boundaries. This section discusses key risk management strategies and important compliance and regulatory considerations when trading on CMC Markets.
Risk Management Techniques
1. Use of Stop-Loss Orders
- Purpose: Stop-loss orders automatically close a trade at a specified level to prevent further losses if the market moves against your position.
- Application: Use tight stop-losses for volatile markets to limit potential losses, and consider wider stop-losses for less volatile markets to allow some room for market movement.
2. Leverage Management
- Strategy: While leverage can amplify gains, it also increases the risk of substantial losses. Manage leverage carefully by not maximizing the allowable leverage and instead trading with leverage levels that align with your risk tolerance.
- Application: Evaluate the impact of leverage on potential losses before opening positions and adjust leverage according to the volatility and risk associated with the market.
3. Diversification
- Purpose: Diversification across different asset classes, markets, or instruments can reduce risk as it spreads exposure, potentially offsetting losses in one area with gains in another.
- Application: On CMC Markets, diversify your portfolio by trading a mix of asset types, such as forex, commodities, indices, and bonds.
4. Regular Monitoring and Review
- Strategy: Constant monitoring of open positions allows you to react swiftly to market changes or unforeseen events.
- Tools: Utilize CMC Markets’ advanced trading tools to set up alerts and keep an eye on market trends and performance metrics.
5. Risk/Reward Ratio
- Consideration: Before entering a trade, evaluate the potential reward relative to the risk. Aim for trades where the potential reward justifies the risk, commonly aiming for a risk/reward ratio of at least 1:2.
- Application: Use technical analysis to identify potential exit points and calculate expected gains versus possible losses to determine if a trade meets your risk/reward criteria.
Compliance and Regulatory Aspects
1. Regulatory Compliance
- Regulation: CMC Markets is regulated by major financial authorities such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) in the UK, ensuring high standards of operational integrity and client protection.
- Importance: Trading with a regulated broker ensures adherence to financial laws and protects against fraud and malpractice.
2. Client Money Protection
- Mechanism: Client funds are held in segregated accounts separate from the company’s funds, providing additional security for traders.
- Benefit: Segregation of funds ensures that client money is not used for company expenses and is available for withdrawal regardless of the financial health of the broker.
3. Data Security
- Concern: Maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of personal and financial data.
- Measures: Ensure that your trading platform uses encryption, secure connections (SSL), and robust cybersecurity measures to protect data.
4. Adherence to Trading Policies
- Best Practices: Be aware of and adhere to all trading policies, terms, and conditions set by CMC Markets.
- Application: This includes understanding how margin calls work, the broker’s policies on slippage and order execution, and procedures for resolving disputes.
By incorporating these risk management techniques and understanding compliance and regulatory requirements, traders can safeguard their investments and operate within a secure and regulated trading environment. Always stay updated with any regulatory changes and continue educating yourself on risk management strategies to enhance your trading on CMC Markets.