Forex trading involves the buying and selling of currencies on the global financial markets and can be a dynamic addition to any investor’s portfolio. CMC Markets is a prominent player in the Forex industry, providing traders with comprehensive resources and tools for currency trading. This guide provides an overview of Forex trading at CMC Markets and underscores the importance of understanding trading fees associated with Forex transactions.
Overview of CMC Markets as a Forex Trading Platform
CMC Markets is renowned for its robust trading technology, extensive range of currency pairs, and competitive market access. Here are key features that make CMC Markets stand out:
Range of Offerings
- Extensive Currency Pairs: CMC Markets offers a broad array of major, minor, and exotic currency pairs, allowing traders to capitalize on fluctuations in global currency markets.
- Advanced Trading Tools: The platform provides advanced charting tools, automated trading capabilities, and up-to-the-minute news and analysis to help traders make informed decisions.
User-Friendly Interface
- Customizable Platform: Both the web and mobile platforms are highly customizable, catering to the needs of both novice and experienced traders.
- Accessibility: CMC Markets offers ease of access with mobile and tablet apps, ensuring traders can manage and execute trades on-the-go.
Educational and Analytical Resources
- Training Resources: CMC Markets places a strong emphasis on education and training, offering webinars, tutorial videos, and comprehensive guides that cover everything from the basics of Forex trading to advanced strategies.
- Market Insights: Traders have access to high-quality analytical tools including technical indicators, expert commentary, and real-time data feeds that help refine their trading strategies.
Importance of Understanding CMC Markets Forex Fees
CMC Markets Forex Fees are an essential aspect of Forex trading that can significantly impact overall profitability. Here’s why understanding these fees is crucial:
Types of Fees
- Spreads: The difference between the buying price and the selling price of a currency pair. CMC Markets offers competitive spreads which can be particularly advantageous for frequent traders.
- Overnight Fees: Also known as swap fees or rollover rates, these are charged when positions are held open overnight. The rate can either be a cost or a gain, depending on the direction of your position and the differential in interest rates between the two currencies traded.
- Commission: Depending on the type of account, CMC Markets may charge a commission per trade in addition to spreads.
Managing Costs
- Cost Efficiency: Understanding and calculating trading costs is crucial for developing cost-efficient trading strategies. Traders need to factor in these costs to determine their net profit from trading activities.
- Strategic Trading: By understanding how fees are structured, traders can choose optimal trading times and adjust their strategies according to the cost implications. For instance, trading during major market hours might offer tighter spreads.
Transparent Pricing
- No Hidden Fees: CMC Markets is known for its transparency in pricing. Traders are advised to review the detailed pricing structure available on the CMC Markets platform to avoid any surprises.
Understanding CMC Markets Forex Fees Structure
Navigating the fee structure of a Forex trading platform is crucial for traders who need to manage their trading expenses effectively. CMC Markets offers a transparent pricing model that includes various types of fees depending on the instruments and the nature of the trades. This guide provides a detailed breakdown of the fee structure for Forex trading at CMC Markets, including explanations of spreads, commissions, and other trading costs.
Detailed Breakdown of the Fee Structure
Spreads
- Definition: Spreads are the difference between the bid (sell) and ask (buy) price of a currency pair. It is essentially the cost charged by the broker for executing a trade.
- CMC Markets Approach: CMC Markets offers competitive spreads starting from as low as 0.7 pips on major currency pairs like EUR/USD. Spreads can vary based on market conditions and the liquidity of the currency pair.
Commissions
- Definition: Commissions are fees charged on a per-trade basis and are common in accounts that provide tighter spreads.
- CMC Markets Approach: CMC Markets primarily offers spread-based trading for most retail traders, which means there are no additional commission fees on top of the spreads for standard accounts. However, professional or institutional accounts might incur commission fees depending on the account type and trading volume.
Overnight Fees (Swap Fees)
- Definition: Also known as rollover rates, these are interest fees that you either earn or pay for holding a position overnight. The fee depends on the difference in interest rates between the two currencies in the pair.
- CMC Markets Approach: CMC Markets charges or credits overnight fees based on the direction of your position and the differential in interest rates. These rates are transparently listed on the trading platform, allowing traders to consider these costs when planning to hold positions overnight.
Other Trading Costs
- Inactivity Fees: If an account is deemed inactive (no trading activity) for a period, CMC Markets may charge an inactivity fee. The specifics of this fee can typically be found in the account terms and conditions.
- Currency Conversion Fees: For trades involving currency pairs not in your account’s base currency, a currency conversion fee may apply. This fee compensates for the cost of converting your profits or losses into your base currency.
- Transactional Costs: While not directly charged as fees, traders should be aware of potential costs associated with deposits and withdrawals, including fees from payment providers or banks.
How to Manage Trading Costs Effectively
- Trade During Peak Hours: Trading during major market hours can lead to tighter spreads due to higher liquidity.
- Monitor Swap Rates: If you plan to hold positions overnight, consider the impact of swap rates on your trading strategy.
- Account Selection: Choose the type of trading account that best fits your trading style. For high-volume traders, an account with lower spreads and commissions may be more cost-effective despite higher initial requirements.
Transparency and Planning
CMC Markets is known for its transparency in fee structures, providing traders with all the necessary information upfront to make informed trading decisions. Traders are encouraged to regularly review and understand the detailed pricing structures available on the CMC Markets platform or to consult with customer support to clarify any doubts about fees and charges.
Comparison of Spreads Across Different Currency Pairs
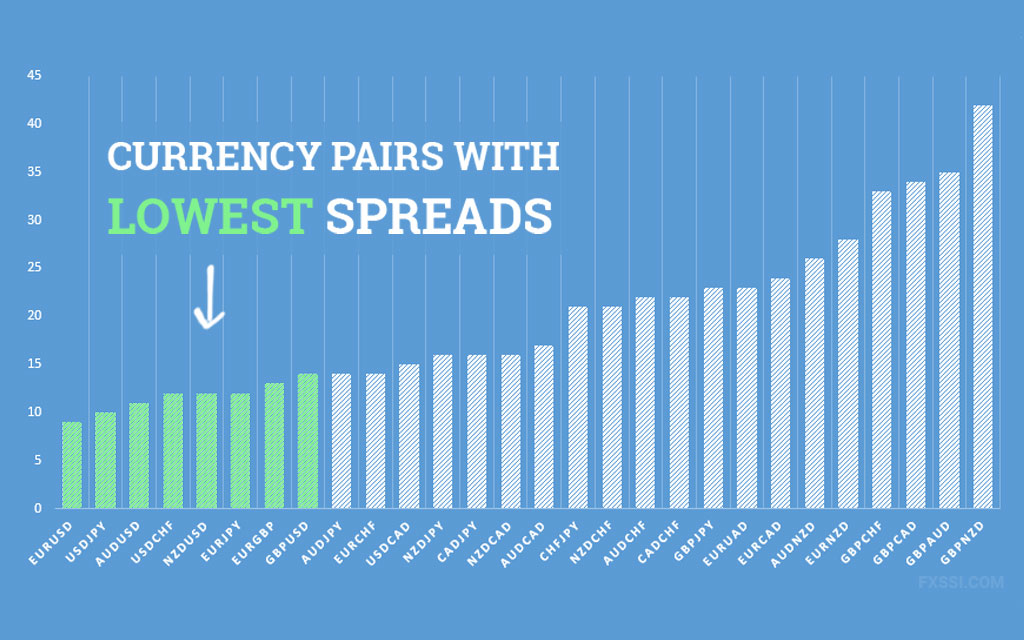
In Forex trading, spreads—the difference between the bid and ask prices—are crucial for traders to understand as they directly impact the cost of trading. Spreads can vary significantly across different types of currency pairs: major, minor, and exotic. Additionally, factors like market volatility and trading hours also play significant roles in determining the spread. Here’s a detailed analysis of how these elements affect spreads and what traders can expect when trading different types of currency pairs with a broker like CMC Markets.
Typical Spreads for Different Currency Pairs
Major Currency Pairs
- Examples: EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, USD/CHF
- Typical Spreads: Major pairs generally have the tightest spreads due to their high liquidity and large trading volume. Spreads can be as low as 0.7 pips for pairs like EUR/USD during active trading hours.
- Characteristics: These pairs are associated with stable economies and less volatility in normal market conditions, leading to narrower spreads.
Minor Currency Pairs
- Examples: EUR/GBP, AUD/NZD, EUR/AUD
- Typical Spreads: Minor or cross currency pairs tend to have slightly wider spreads than major pairs, often ranging from 2 to 10 pips, depending on market conditions and liquidity.
- Characteristics: These involve less frequently traded currencies than the majors but are still relatively stable and liquid.
Exotic Currency Pairs
- Examples: USD/SGD, EUR/TRY, GBP/ZAR
- Typical Spreads: Exotic pairs usually have the widest spreads, which can range significantly, sometimes reaching as high as 50 pips or more.
- Characteristics: Exotics involve currencies from emerging markets or smaller economies. They are less liquid, more volatile, and carry higher transaction costs.
Factors Influencing Spreads
Market Volatility
- Impact: High volatility can lead to wider spreads due to increased uncertainty and risk. Market-moving events such as economic announcements, geopolitical developments, or financial crises typically increase volatility and thus spreads.
- Strategy: Traders should be aware of scheduled economic events and adjust their trading strategies and times accordingly to manage costs.
Trading Hours
- Impact: Spreads are generally tighter during the main trading hours of the Forex markets, which correspond to the business hours of the respective financial centers (London, New York, and Tokyo).
- Overlap Hours: The tightest spreads often occur during the overlap between the New York and London trading sessions, as this is when liquidity is at its highest.
- Strategy: To capitalize on narrower spreads, traders might prefer executing trades during these peak hours.
How to Manage Spread-Related Costs
- Trade Major Pairs: Focus on trading major currency pairs during high liquidity hours to benefit from lower spreads.
- Monitor News and Events: Keep an eye on economic calendars and news releases that can affect market volatility and hence spreads.
- Use Limit Orders: Limit orders can help manage costs by setting a maximum acceptable purchase price or minimum acceptable sale price, which can protect against widening spreads in volatile markets.Impact of Leverage on Trading Fees
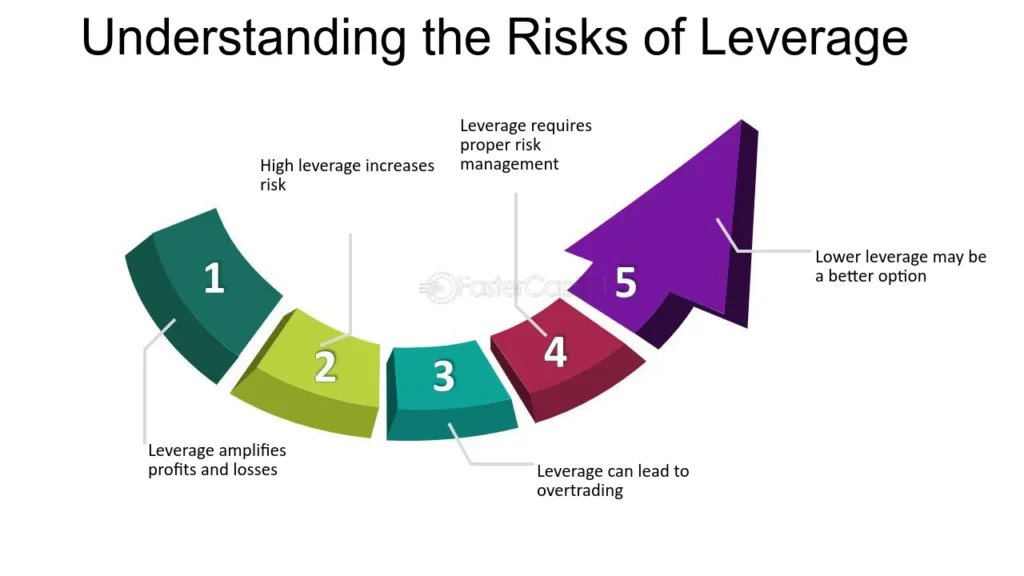
Leverage is a powerful tool in forex trading that allows traders to control larger positions with a relatively small amount of capital. However, while leverage can significantly increase the potential for profit, it also amplifies the risks and can impact the overall cost per trade. Understanding how leverage at CMC Markets affects your trading costs and how to manage the associated risks is crucial for effective trading.
How Leverage Affects Cost Per Trade at CMC Markets
Amplification of Transaction Costs
- Spread Costs: Leverage does not directly change the spread (the cost built into each trade as the difference between the buy and sell price of the currency pair), but it does amplify the impact of the spread cost relative to your account balance. For example, if you are trading a large position with high leverage, the absolute amount paid as spread on this larger position increases, even though the spread as a number of pips remains the same.
- Overnight Fees (Swap Rates): When you use leverage, you are essentially borrowing money to open a larger position. If this position is held overnight, you incur swap rates. These fees can accumulate significantly, especially on large leveraged positions held over multiple days.
Example Calculation
Suppose you open a $100,000 position in EUR/USD, using 100:1 leverage with only $1,000 of your own capital. If the spread is 1 pip (equivalent to $10 on a standard lot of $100,000 in EUR/USD):
- Without Leverage: You would need the full $100,000, and the cost of the spread would still be $10, a minimal percentage of your trading capital.
- With Leverage: You still pay $10 for the spread, but now it represents a higher percentage of your actual investment ($1,000), increasing the relative cost of the trade.
Managing Risks Associated with High Leverage
Understanding Leverage Implications
- Market Volatility: High leverage can lead to significant losses, especially in volatile market conditions. A small adverse move in currency prices can result in substantial losses relative to the trader’s investment.
Effective Risk Management Strategies
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: To limit potential losses, always use stop-loss orders. This is crucial when employing high leverage, as it helps prevent your account from suffering a devastating loss from an unexpectedly large market move.
- Conservative Leverage Use: Just because high leverage is available doesn’t mean it’s advisable to use it to the fullest. Consider using lower levels of leverage or adjusting leverage according to the volatility and risk associated with the currency pair you are trading.
- Regular Monitoring: Keep a close eye on open positions, especially if you are using significant leverage. Be prepared to act quickly to close a position if the market moves unfavorably.
- Margin Buffer: Maintain a margin buffer in your account to avoid margin calls that can occur if your account equity falls below the required level due to trading losses. This buffer acts as a financial cushion against volatile market movements.
Educational Resources and Tools
- Leverage Calculators: Utilize tools provided by CMC Markets to calculate and understand the impact of leverage on potential trading costs and account equity.
- Training and Webinars: Take advantage of educational resources to better understand leverage and its effects. CMC Markets often offers training sessions and webinars on effective leverage use and risk management.

Commissions and Additional Charges at CMC Markets
Understanding the complete fee structure, including any commission fees and additional charges, is crucial for traders to manage their finances effectively while trading with CMC Markets. This section provides a detailed explanation of the various fees that may be incurred, helping traders plan their trading activities and budget accordingly.
Commission Fees Charged by CMC Markets Forex Fees
Forex Trading
- Spread-based Trading: CMC Markets primarily offers spread-based pricing for its Forex trading. This means traders pay no direct commissions but are subject to the spread costs between the buy and sell prices of currency pairs.
- Commission-based Trading: For certain account types or trading platforms (especially for professional or institutional traders), CMC Markets may charge a commission. This is usually a fixed rate per lot traded and is in addition to the spread. Such arrangements are typically transparently detailed in the account setup.
CFD Trading
- Equity CFDs: Commission fees are typically charged for trading CFDs on shares. These fees are generally a percentage of the trade value or a fixed amount per trade, depending on the region and the market being traded.
Transparency
- CMC Markets is known for its transparency in pricing. Detailed information on all applicable trading fees, including any commissions for specific instruments or accounts, is available on their website or directly through customer service.
Additional Charges
Inactivity Fees
- Purpose: To cover the costs associated with maintaining accounts that have no trading activity over a certain period.
- How It’s Charged: If an account has no trading activity for a period (usually 12 months or more), CMC Markets may charge a monthly inactivity fee. The specific terms, including the fee amount, are outlined in the client agreement.
Withdrawal Fees
- Bank Transfers: There may be charges for withdrawals, especially when requesting multiple withdrawals in a month or international bank transfers.
- Credit/Debit Cards and E-Wallets: Fees may vary depending on the method used and the jurisdiction. Often, the first withdrawal of the month is free, with subsequent withdrawals incurring a charge.
Currency Conversion Fees
- When Applicable: If you trade a product denominated in a currency different from your account’s base currency, CMC Markets may apply a currency conversion charge.
- Calculation: This fee is usually a small percentage of the trade’s value and is applied every time a trade is opened or closed in a currency different from the account’s base.
Overnight Funding Charges
- Swap/Rollover Fees: For positions held open overnight, CMC Markets charges funding fees, which can either be a cost or a credit, based on the direction of your position and the differential in interest rates between the two currencies involved.
Tips for Managing Fees and Charges
- Regular Review: Keep a close watch on your account statements and the fees charged. Understanding these in detail can help in planning trades to minimize costs.
- Active Trading Management: Avoid inactivity fees by managing your trading frequency and ensuring regular activity in your account.
- Withdrawal Planning: Plan your withdrawals to minimize fees, potentially consolidating multiple withdrawals into fewer transactions.
How to Calculate Trading Costs in CMC Markets Forex Fees
Calculating your total trading costs is essential for effective trading strategy and financial planning. This guide will provide a step-by-step approach to calculate trading costs, including spreads, commissions (if applicable), and other potential costs using examples with real currency pairs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Trading Costs
1: Identify the Cost Components
- Spreads: The difference between the bid (sell) price and the ask (buy) price of a currency pair.
- Commissions: Fixed fees charged per trade or per lot, based on the account type and trading platform.
- Swap Fees: Fees for holding a position overnight, which can either be a charge or a credit.
2: Calculate Spread Costs
- Formula: Spread Cost = Spread size in pips × Pip value × Number of lots traded
- Example: Trading EUR/USD with a spread of 1 pip on a standard lot (100,000 units):
- Pip Value: For EUR/USD, one pip typically equals $10 per standard lot.
- Calculation: 1 pip × $10/pip × 1 lot = $10
3: Calculate Commission Costs
- Formula: Commission Cost = Commission per lot × Number of lots
- Example: If the commission is $5 per standard lot:
- Calculation: $5 × 1 lot = $5
4: Factor in Swap Fees (if applicable)
- Example: Holding a EUR/USD position overnight incurs a swap fee of $0.50 per lot.
- Calculation: $0.50 × 1 lot = $0.50
5: Calculate Total Trading Costs
- Formula: Total Trading Cost = Spread Cost + Commission Cost + Swap Fee
- Example: Total cost for one standard lot of EUR/USD, held overnight:
- Calculation: $10 (spread cost) + $5 (commission) + $0.50 (swap fee) = $15.50
6: Consider Additional Factors
- Slippage: Difference between the expected price of a trade and the price at which the trade is executed. Add an estimate for slippage based on historical data if available.
- Currency Conversion Fees: If your account currency differs from the currency pair traded, conversion fees may apply.
Examples Using Real Currency Pairs
Major Currency Pair: USD/JPY
- Assumptions:
- Spread: 0.8 pips
- Commission: $4 per lot
- Swap fee: $0.30 per lot
- Calculations:
- Spread Cost: 0.8 pips × $9/pip (approximate pip value for USD/JPY per lot) × 1 lot = $7.20
- Commission Cost: $4 × 1 lot = $4
- Swap Fee: $0.30 × 1 lot = $0.30
- Total Trading Cost: $7.20 + $4 + $0.30 = $11.50
Exotic Currency Pair: USD/ZAR
- Assumptions:
- Spread: 100 pips
- Commission: $10 per lot
- Swap fee: $1.50 per lot
- Calculations:
- Spread Cost: 100 pips × $0.70/pip (approximate pip value for USD/ZAR per lot) × 1 lot = $70
- Commission Cost: $10 × 1 lot = $10
- Swap Fee: $1.50 × 1 lot = $1.50
- Total Trading Cost: $70 + $10 + $1.50 = $81.50
Fee Reduction Strategies
Minimizing trading fees is crucial for enhancing the profitability of your trading activities. By adopting specific strategies and best practices, traders can significantly reduce the impact of fees on their trading accounts. Here are some effective tips and strategies to minimize trading fees and optimize cost-efficiency.
Strategies to Minimize CMC Markets Forex Fees
1. Trade During High Liquidity Times
- Rationale: Spreads are typically narrower during high liquidity times such as when major market sessions overlap (e.g., New York and London). Tighter spreads mean lower direct costs per trade.
- Implementation: Schedule trades for times when liquidity is highest to take advantage of reduced spreads.
2. Use Limit Orders
- Rationale: Limit orders can help you control the maximum price you pay or the minimum price you receive when entering or exiting trades. This can prevent slippage, where the execution price differs from the expected price, thereby managing the cost.
- Implementation: Set buy limit orders below the market price and sell limit orders above the market price to manage entry and exit prices effectively.
3. Consolidate Trades
- Rationale: Making fewer, larger trades can reduce the total number of commissions paid compared to making many smaller trades, as commissions are typically charged per trade or lot.
- Implementation: Plan your trading strategy to accumulate positions and execute them in larger blocks rather than executing numerous small trades.
4. Choose a Cost-Effective Brokerage Plan
- Rationale: Some brokers, including CMC Markets, offer different account types that vary in cost structure, suitable for different trading styles. For example, accounts with higher balance requirements might offer lower spreads and commissions.
- Implementation: Evaluate the costs associated with different brokerage accounts and select one that aligns with your trading frequency and volume to minimize costs.
5. Avoid Excessive Trading
- Rationale: Overtrading can lead to unnecessarily high transaction costs and can erode potential profits.
- Implementation: Develop a disciplined trading plan and adhere to it strictly to avoid making impulsive trades that are not part of your strategy.
6. Monitor and Plan for Swap Costs
- Rationale: Holding positions overnight can incur swap fees which can add up, especially when using leverage.
- Implementation: Be aware of the swap rates provided by your broker and plan your trading strategy to close positions that might incur high swap costs unless justified by potential gains.
Best Trading Practices for Cost-Efficiency
1. Regular Review of Costs
- Practice: Regularly review all trading receipts and statements to monitor the fees and costs associated with your trades.
- Benefit: This allows you to adjust your trading strategies if you notice that certain types of trades or times are consistently more expensive.
2. Use of Technology
- Practice: Utilize trading tools and technologies that can automate the monitoring of costs and execution of strategies.
- Benefit: Automation can help maintain discipline in your trading approach, ensuring you stick to cost-effective strategies.
3. Continual Education
- Practice: Stay informed about changes in brokerage fees, market conditions, and other factors that can influence trading costs.
- Benefit: Being well-informed enables you to adapt your trading strategies to changing conditions to maintain cost-efficiency.
Comparing CMC Markets with Other Brokers
When choosing a Forex broker, one of the critical factors to consider is the fee structure. This comparison will highlight how CMC Markets stacks up against other popular Forex brokers in terms of fees, helping traders make an informed decision based on cost-effectiveness.
Fee Comparison Between CMC Markets Forex Fees and Other Forex Brokers
To provide a comprehensive view, we’ll consider typical fees such as spreads, commissions, and additional charges like inactivity fees and withdrawal fees.
Spread and Commission Fees
- CMC Markets: Known for competitive spreads, particularly on major currency pairs like EUR/USD, where spreads can start as low as 0.7 pips. CMC primarily offers spread-only pricing but may charge commissions for certain types of trades or accounts.
- Broker A (e.g., IG Markets): Typically offers spreads starting from about 0.8 pips on major pairs. IG Markets may also include a fixed commission on trades depending on the account type.
- Broker B (e.g., Forex.com): Offers variable spreads starting from 1.0 pip on major currency pairs and may charge a low commission on trades depending on the platform used.
- Broker C (e.g., Saxo Bank): Generally offers higher minimum spreads starting from about 0.6 pips for major pairs but includes a commission that varies by volume.
Inactivity Fees
- CMC Markets: Charges an inactivity fee if the trading account is inactive for a period, typically around 12 months, which can be around $10 to $15 per month.
- IG Markets: Similar to CMC Markets, IG charges a monthly inactivity fee after two years of no trading activity.
- Forex.com: Might charge a monthly inactivity fee after one year of inactivity, usually a bit higher than CMC Markets.
- Saxo Bank: Known for a high inactivity fee if no trades are made over a period, typically charging after 6 months of inactivity.
Withdrawal Fees
- CMC Markets: Usually does not charge for withdrawals, but fees can be applied by financial institutions for wire transfers.
- IG Markets: Offers a number of free withdrawals per month before charging.
- Forex.com: May charge for wire withdrawals depending on the region.
- Saxo Bank: Typically charges a fixed fee for withdrawals.
Choosing the Right Broker Based on Fee Structures
When deciding on a broker based on fees, consider the following factors:
Trading Volume and Frequency
- High-volume traders might benefit from a broker with lower spread costs and volume-based commissions, while occasional traders might prioritize lower inactivity fees.
Trading Strategy
- Scalpers and day traders should look for lower spread and commission rates due to the high number of trades they execute.
- Swing traders and long-term investors might focus more on overnight fees and inactivity charges.
Account Types Offered
- Some brokers offer multiple account types that can significantly vary in terms of fee structures. Assess whether an account type aligns with your trading style and financial goals.
Total Cost of Trading
- Consider all possible costs, including spreads, commissions, inactivity fees, withdrawal fees, and any other administrative charges.
Transparency and Other Services
- Choose a broker that not only offers competitive CMC Markets Forex Fees but also provides transparency in their fee structure, along with robust trading tools, educational resources, and excellent customer support.

CMC Markets Forex Fees Changes and Updates
Staying informed about changes to fee structures is crucial for effectively managing your trading costs and strategy. This section will guide you on how to stay updated with CMC Markets’ fee changes and understand the historical trends and their impact on traders.
How to Stay Informed About Fee Structure Changes
1. Regularly Check the Official Website
- Action: Visit CMC Markets’ official website frequently. Most brokers update their fee information on their sites, including details on spreads, commissions, and other charges.
- Benefit: Ensures you receive the most accurate and up-to-date information directly from the source.
2. Subscribe to Email Notifications
- Action: Sign up for newsletters and alerts from CMC Markets. Brokers often send updates about changes to their fee structures or trading conditions via email.
- Benefit: Convenient way to receive updates directly in your inbox, helping you stay proactive about any changes.
3. Follow Social Media and Blogs
- Action: Follow CMC Markets on social media platforms and read their blogs if available. Brokers frequently use these channels to communicate news and updates.
- Benefit: Provides additional insights into the broker’s activities and market analysis, alongside updates about fees.
4. Contact Customer Support
- Action: If unclear about certain fee changes, contact CMC Markets’ customer support for clarification.
- Benefit: Direct interaction can provide specific answers and explanations, ensuring that you fully understand how the changes impact your trading.
5. Attend Webinars and Online Training Sessions
- Action: Participate in webinars and online sessions hosted by CMC Markets.
- Benefit: These sessions not only address changes but often provide training on how to adjust your trading strategies in response to these changes.
Historical Fee Trends and Their Impact on Traders
Overview of Trends
- Reduction in Trading Costs: Over the past decade, there has been a competitive push across the industry leading to generally lower spreads and commissions. This trend has been driven by technological advancements and increased market competition.
- Introduction of New Fee Types: As regulators crack down on certain types of trading incentives, brokers have adapted by introducing new fee types, such as inactivity fees or increased costs for premium services.
Impact on Traders
- Lower Trading Costs: Historically, the reduction in basic trading costs (like spreads and commissions) has made Forex trading more accessible and cost-effective for retail traders.
- Increased Transparency: Regulatory changes have forced brokers to become more transparent about their fee structures, benefiting traders who can now make more informed decisions.
- Adaptation to New Costs: Traders have had to adjust their strategies not only to optimize trading costs but also to account for other fees like inactivity or withdrawal fees that might impact their overall profitability.
Proactive Measures
- Review and Adjust: Regularly review your trading costs against your trading outcomes to ensure that fee changes do not negatively impact your profitability.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Always perform a cost-benefit analysis when considering changes in your trading strategy or broker based on fee adjustments.

FAQs and Tips for Forex Traders on CMC Markets Forex Fees
Navigating the complexities of Forex trading with CMC Markets involves understanding the fees, trading costs, and strategies to enhance performance while managing these expenses. Here, we compile some commonly asked questions and provide expert tips to help traders optimize their trading activities.
Commonly Asked Questions About Fees and Trading Costs
What are the typical spreads for major currency pairs on CMC Markets?
- Answer: CMC Markets offers competitive spreads starting from as low as 0.7 pips for major currency pairs like EUR/USD, depending on market conditions and liquidity.
Are there any commissions on Forex trades with CMC Markets?
- Answer: Typically, CMC Markets charges no commissions on Forex trades as they primarily operate on a spread-based fee structure. However, commissions may apply for certain types of accounts or high-volume traders.
Does CMC Markets charge inactivity fees?
- Answer: Yes, CMC Markets may charge a monthly inactivity fee if your account has not executed any trades for a set period, usually 12 months. The fee is designed to cover the cost associated with maintaining inactive accounts.
How are overnight fees calculated at CMC Markets?
- Answer: Overnight fees, or swap fees, are charged on positions held open overnight and are calculated based on the differential interest rates of the currencies involved in the trade. These rates can vary daily based on market conditions.
Can I trade micro-lots with CMC Markets?
- Answer: Yes, CMC Markets allows trading in micro-lots, which is particularly beneficial for traders with smaller account sizes who wish to manage their risk more effectively.
Expert Tips to Enhance Trading Performance While Managing Fees
1: Trade During High Liquidity Times
- Rationale: Trading during periods of high liquidity, such as the London or New York session overlaps, typically results in lower spreads and better execution.
- Action: Plan your trading schedule around these times to take advantage of tighter spreads and potentially lower trading costs.
2: Utilize Limit and Stop Orders
- Rationale: Proper use of limit and stop orders can help manage risks and lock in profits without needing to monitor the markets continuously.
- Action: Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and take-profit orders to secure profits at desired levels, ensuring that these settings consider the current spread and potential slippage.
3: Monitor and Adapt to Fees
- Rationale: Staying informed about any changes in the fee structure is crucial for managing your trading costs effectively.
- Action: Regularly check the CMC Markets website for updates on spreads, commissions, and other fees. Adjust your trading strategy accordingly to maintain profitability.
4: Optimize Your Trading Strategy
- Rationale: An effective trading strategy considers not only the market conditions but also the cost implications of executing trades.
- Action: Review your trading performance periodically to ensure that transaction costs are not eroding your profits. Consider whether a strategy adjustment is warranted based on performance and cost analysis.
5: Educate Yourself Continuously
- Rationale: The Forex market is dynamic, and continuous education can provide you with new strategies and insights to improve your trading.
- Action: Take advantage of the educational resources offered by CMC Markets, including webinars, tutorials, and articles, to stay informed about market trends, trading techniques, and ways to manage costs effectively.

